Figure 4.
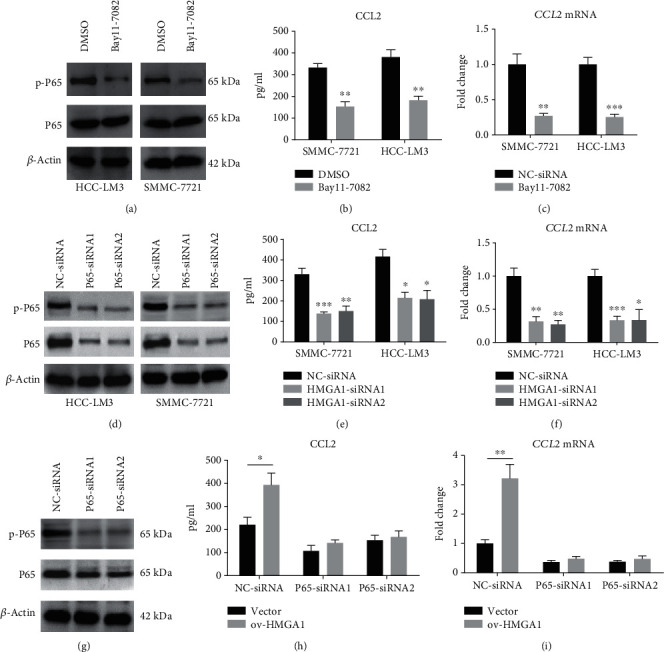
HMGA1 regulates CCL2 expression in an NF-κB-dependent manner. (a) Western blotting analysis showed the total and phosphorylated level of P65 in HCC-LM3 and SMC-7721 cells after treatment with NF-κB inhibitor Bay11-7082 (10 μM). (b) ELISA analysis showed the secreted level of CCL2 in the conditioned medium (CM) of HCC-LM3 and SMC-7721 cells after treatment with 10 μM Bay11-7082 for 24 h. (c) Real-time qPCR analysis showed the mRNA level of CCL2 in the HCC-LM3 and SMC-7721 cells after treatment with 10 μM Bay11-7082 for 24 h. (d) Western blotting analysis showed the total and phosphorylated level of P65 in HCC-LM3 and SMC-7721 cells after treatment with specific siRNAs against P65. (e) ELISA analysis showed the secreted level of CCL2 in the conditioned medium (CM) of HCC-LM3 and SMC-7721 cells after treatment with specific P65 siRNAs for 48 h. (f) Real-time qPCR analysis showed the mRNA level of CCL2 in the HCC-LM3 and SMC-7721 cells after treatment with specific P65 siRNAs for 48 h. (g) Western blotting analysis showed the total and phosphorylated level of P65 in SNU-423 cells after treatment with specific siRNAs against P65. (h) ELISA analysis showed the secreted level of CCL2 in the conditioned medium (CM) of ov-vector and ov-HMGA1 SNU-423 cells after treatment with specific P65 siRNAs for 48 h. (i) Real-time qPCR analysis showed the mRNA level of CCL2 in the ov-vector and ov-HMGA1 SNU-423 cells after treatment with specific P65 siRNAs for 48 h. The ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey's multiple comparison test or the Student's t-test was used for group comparisons. ∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001.
