Fig. 5.
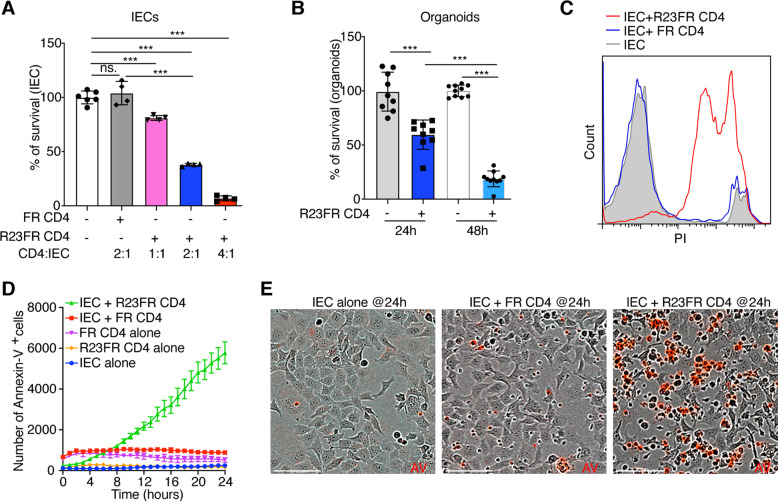
Intestinal CD4+ T cells from R23FR mice with colitis kill IECs ex vivo. CD4+ T cells obtained from the large intestines of R23FR mice and FR mice at Day 56 were used for ex vivo cytotoxicity assays. A Relative survival of target epithelial cells after coculture with CD4+ T cells from R23FR and FR mice for 24 h as determined using a CellTiter-Glo Luminescent Cell Viability Assay Kit with different effector:target ratios. n = 4–6. Each dot represents one well/condition from a representative of four independent experiments with similar results. B Relative survival of target intestinal enteroids after coculture with CD4+ T cells from R23FR mice for 24 h and 48 h as determined using a CellTiter-Glo Luminescent Cell Viability Assay Kit (effector:target ratio = 4:1). n = 9–10. Each dot represents one well/condition from a representative of three independent experiments with similar results. C Flow cytometric analysis of the number of dead epithelial (PI+Epcam+) cells after culture of IECs with colonic CD4+ T cells from R23FR or FR mice at Day 56 (effector:target ratio = 4:1) for 24 h. The data represent two independent experiments. D IncuCyte kinetic quantification of apoptotic (Annexin V+) cells under different conditions. IEC alone, CD4+ T cells from R23FR or FR mice alone and IECs cultured with CD4+ T cells from R23FR or FR mice (effector:target ratio = 2:1). The data are expressed as the average of the events per well (n = 6 wells/condition). E Representative IncuCyte images of Annexin V+ cells (AV, red) showing IECs alone and IECs cocultured with colonic CD4+ T cells from control FR mice or from R23FR mice. Ns, not significant, ***p < 0.001, by nonparametric Mann–Whitney test. Scale bars = 100 μm in (E)