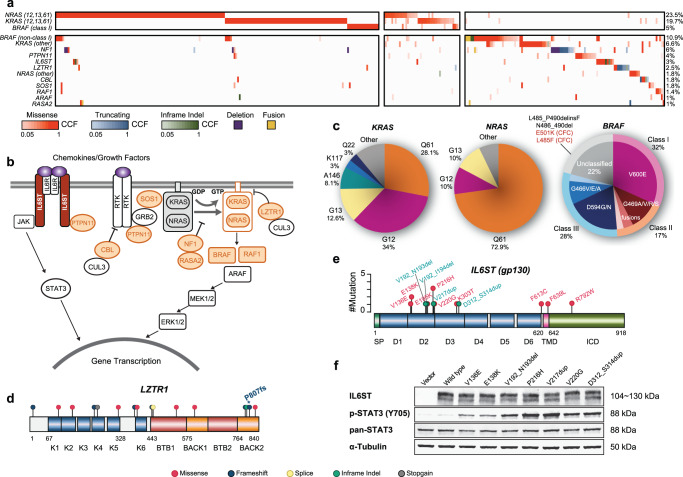
Fig. 3. Alterations of the RAS-MAPK and JAK-STAT3 pathway in relapsed refractory multiple myeloma.
a Heatmap of RAS-RAF pathway alterations in cases with at least one mutation with CCF (cancer cell fraction) ≥0.05 (n = 354) (Methods). Clonal mutations of RAS and BRAF (RAS Q61, G12, G13, and BRAF V600) showed a strict pattern of mutual exclusivity (top left panel). Mutations which appeared to co-occur were subclonal and likely belonged to different clones (top middle panel). There was also a distinct group of cases with mutations associated with the Rasopathies (bottom right panel). IL6ST was also included given the reported association with SHP2 (PTPN11) b Overview of the RAS-RAF signaling pathway and summary of alterations observed in RRMM. Rasopathy-associated genes that had mutations in our RRMM cohort are highlighted in light orange. c Pie charts show the distribution of mutations in NRAS, KRAS, and BRAF across our RRMM cohort. d Lollipop plot of LZTR1 which was enriched for loss-of-function mutations. e Lollipop plot of mutations in IL6ST. f JAK-STAT3 pathway activation in HEK-293FT cells overexpressing IL6ST mutants. Western blot analyses of protein levels of IL6ST, phosphorylated STAT3(Y705); total STAT3, and a-tubulin (loading control) are shown. The experiment was repeated twice independently with similar results. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.