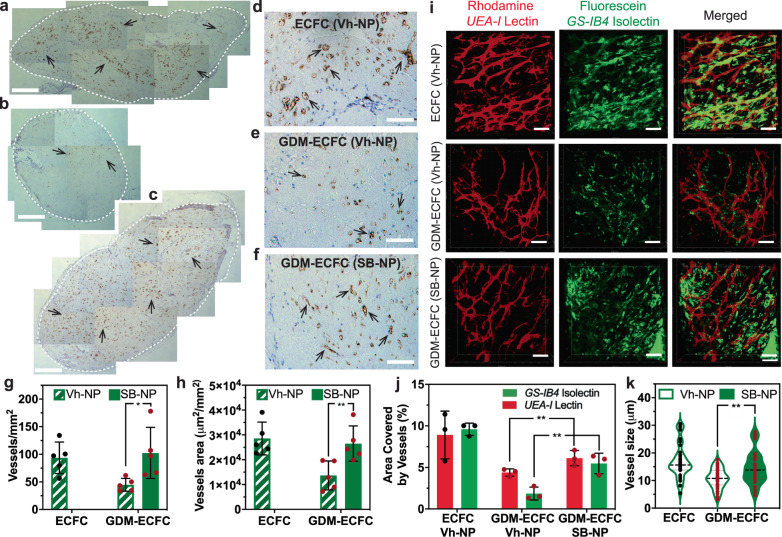
Fig. 6. In vivo functionality of ECFCs conjugated with bioactive nanoparticles.
Normal and GDM-ECFCs were conjugated with nanoparticles containing either vehicle (Vh) or 40 µM SB-431542 (SB). Conjugated ECFCs (100,000 cells/gel) were encapsulated in collagen/fibronectin gels for 48 hr to form vascularized networks and then transplanted into the side flanks of NOD/SCID mice (n = 4-6 animals/group). Representative IHC images stained with anti-human CD31 illustrate the graft harvested 14 days following transplantation (highlighted in white dotted circle) for (a) ECFCs (Vh-NP), (b) GDM-ECFCs (Vh-NP), and (c) GDM-ECFCs (SB-NP). Scale bars are 500 µm. Representative high magnification IHC images of grafts from (d) ECFCs (Vh-NP), e GDM-ECFCs (Vh-NP), and (f) GDM-ECFCs (SB-NP) after 14 days implantation into NOD/SCID mice stained with anti-human CD31 (brown). Arrows indicate human CD31+ vessels, which are perfused with murine erythrocytes. Scale bars are 30 µm. The number and size of human CD31+ vessels were quantified and plotted. Compared to the Vh-NPs control, SB-NPs conjugation increases (g) vessel density (*P = 0.011) and (h) vessel area (**P = 0.0058) formed by GDM-ECFCs in vivo. Five animals (n = 5; mean ± s.d.) were used to evaluate each group: normal ECFCs (black data dots) and GDM-ECFCs (red data dots). i Representative intravital images of grafts pre-perfused with rhodamine-conjugated UEA-I lectin to stain the human vessels (in red) and fluorescein-conjugated GS-IB4 to stain the mouse vessels (in green). 3D confocal rendering demonstrated the interaction between human vasculature (in red) and mouse vasculature (in green) for normal ECFC, GDM-ECFCs conjugated with Vh-NPs and GDM-ECFCs conjugated with SB-NPs. Scale bars are 40 µm. j Vessel quantification and analysis reveal the percent area covered by human vasculature (UEA-I lectin) and mouse vasculature (GS-IB4 isolectin). SB-NPs conjugation to GDM-ECFCs results in the significant increase of both human vessels (**P = 0.021) and mouse vessels (**P = 0.006) that were interconnected to each other. Three animals (n = 3; mean ± s.d.) were used to evaluate each group: normal ECFCs (black data dots) and GDM-ECFCs (red data dots). k Vessel quantification reveals the size distribution of the vessels found in the explant for normal ECFCs, GDM-ECFCs conjugated with Vh-NPs and GDM-ECFCs conjugated with SB-NPs. Compared to the Vh-NPs control, SB-NPs conjugation results in an increase in the mean of vessel size distribution from for GDM-ECFCs (**P = 0.0018).