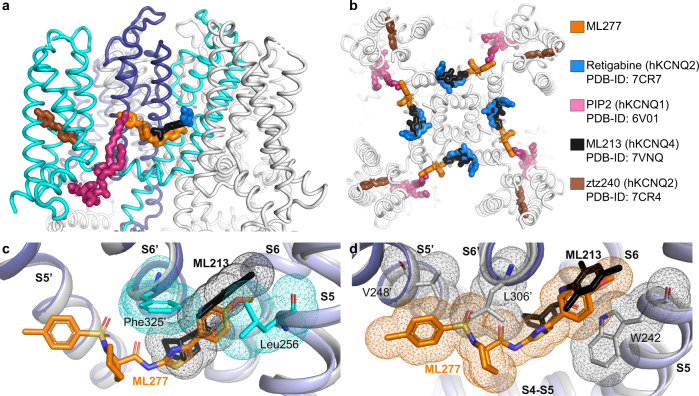
Fig. 6. Binding of ML277 and other KCNQ regulators to xKCNQ1 and hkCNQ4.
a, b Overview of published KCNQ-ligand binding plotted on the xKCNQ1-CaM-ML277 structure. Different isoform structures were aligned based on the pore-forming domain. a View from within the plane of the membrane. Cyan and blue for the two subunits comprising the ML277 binding pocket. b Top view from the extracellular side clipped at the level of the ML277/ML213/retigabine binding sites for clarity. c Superposition of hKCNQ4-CaM-ML213 (gray) onto xKCNQ1-CaM-ML277 (different shades of blue for different subunits, xKCNQ1 residue side chains shown in cyan) ML277 is shown in orange, and ML213 in black. Van der Waals surfaces indicate potential clashes. d Superposition of xKCNQ1-CaM-ML277 onto hKCNQ4-CaM-ML213 (ML213 in black and hKCNQ4 residue side chains in gray). Van der Waals surfaces indicate potential clashes between ML277 and hKCNQ4 residues W242, L306′ and V248′.