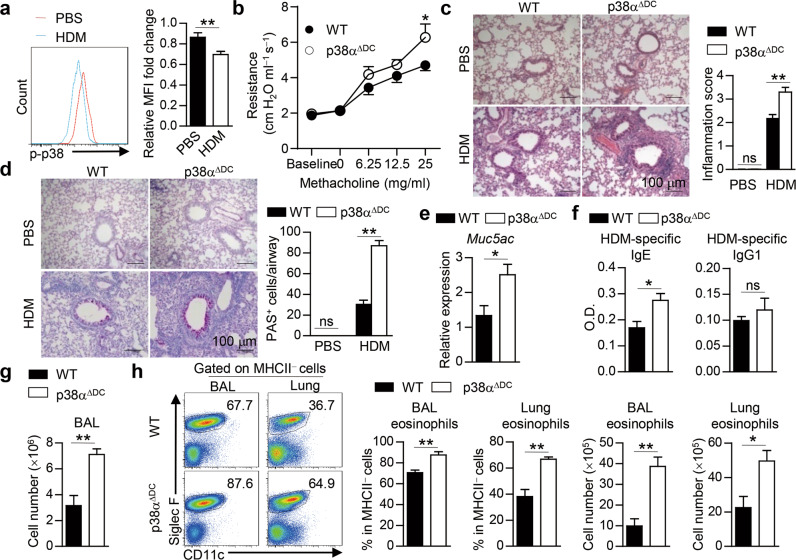
Fig. 1.
DC-specific p38α deletion renders mice susceptible to HDM-induced allergic asthma. a WT mice were i.n. sensitized with HDM for 24 h, and the activity of p38 in lung DCs (CD11c+MHCIIhigh) was examined by flow cytometry and is presented relative to that of lung DCs from PBS-treated mice, which was set as 1 (n = 11–14).b–h WT and p38αΔDC mice were sensitized with HDM on Days 0–2 and challenged with HDM on Days 14–16. Mice were sacrificed for analysis on Day 17 (b, n = 7; c–h, n = 4).Airway resistance was measured (b). H&E (c) and PAS (d) staining of lung sections and quantification. Scale bars represent 100 μm. The expression of Muc5ac in lung tissues was detected by qPCR (e). Serum HDM-specific IgE and IgG1 were detected by ELISA (f). Total cell number in the BALF (g). The percentage and cell number of eosinophils were detected by flow cytometry (h). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ns, not significant. Data are pooled from four experiments (a) or representative of two (b) or three (c–h) independent experiments with consistent results. Student’s t test (a, e–h) or two-way ANOVA (b–d) was performed, and the data are presented as the mean ± SEM