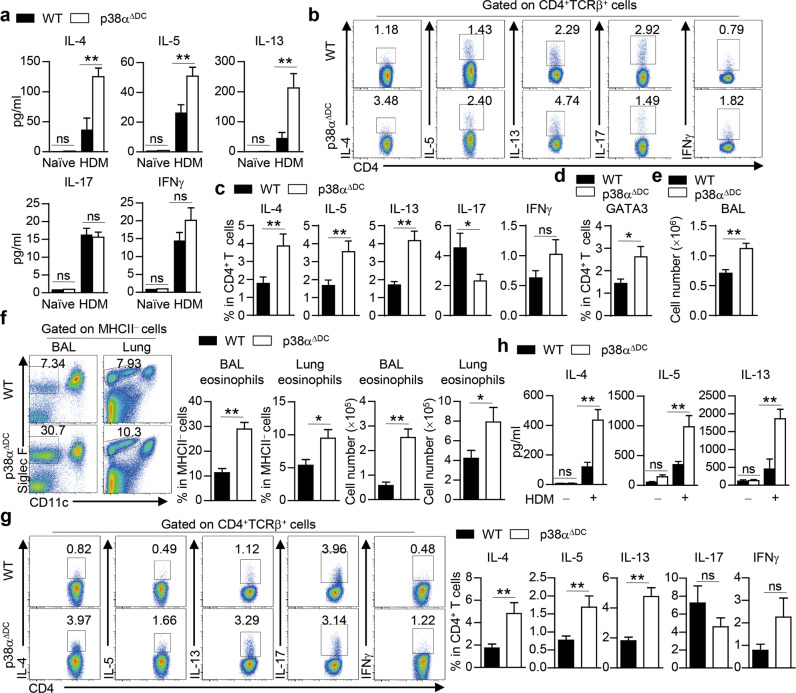
Fig. 2.
p38α deletion in DCs promotes Th2 priming and allergic inflammation during the sensitization phase. a–c WT and p38αΔDC mice were sensitized with HDM on Days 0–2 and challenged with HDM on Days 14–16. Mice were sacrificed for analysis on Day 17. ELISA analysis of IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, IL-17 and IFNγ production in the BALF (a) (n = 3–4). The percentages of IL-4+, IL-5+, IL-13+, IL-17+ and IFNγ+ cells in CD4+ T cells were determined by intracellular staining (b, c) (n = 13). Percentages of GATA3+ cells in CD4+ T cells (d) (n = 5). e–h WT and p38αΔDC mice were sensitized with HDM for 3 days and analyzed 7 days later. Total cell number in the BALF (e) (n ≥ 14). The percentage and cell number of eosinophils were detected by flow cytometry (f) (n ≥ 14). The percentages of IL-4+, IL-5+, IL-13+, IL-17+ and IFNγ+ cells in CD4+ T cells were determined by intracellular staining (g) (n ≥ 19). ELISA analysis of ex vivo-isolated mLN cells restimulated with or without HDM for 72 h (h) (n = 3–4). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ns, not significant. Data are representative of three (a, d, h) independent experiments or pooled from three (b–c, e and f) or four (g) experiments with consistent results. Student’s t test (c–g) or two-way ANOVA (a and h) was performed, and the data are presented as the mean ± SEM