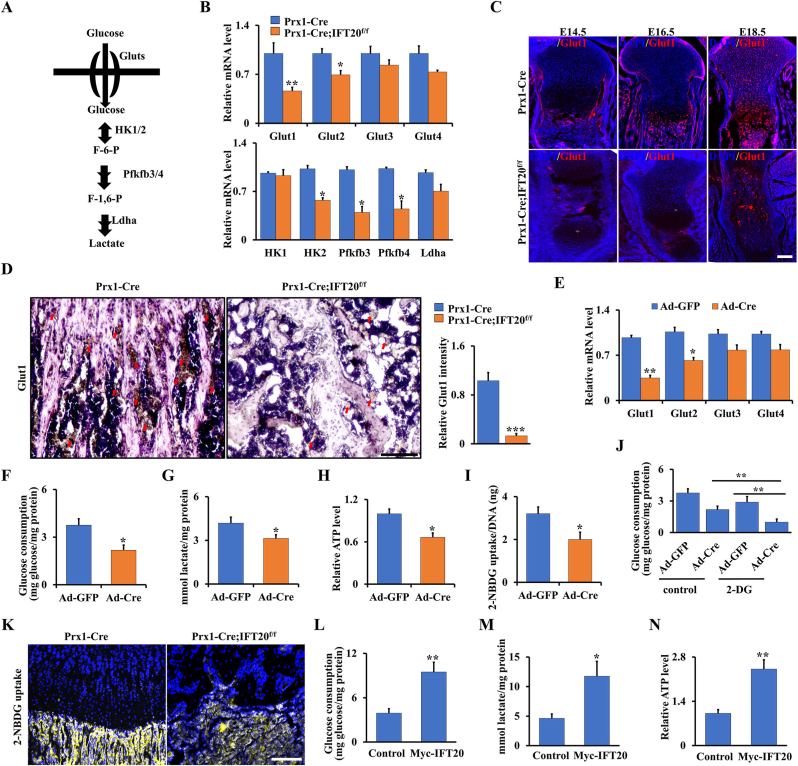
Fig. 6.
IFT20 promotes glucose uptake and glycolysis in MSCs through Glut1 signaling. (A) Diagram of the key enzymes in the glucose metabolism such as Gluts, Hk1/2, Pfkfb3/4 and Ldha. (B) qRT-PCR analysis of glucose metabolism-related genes (Glut1/2/3/4, Hk1/2, Pfkfb3/4, and Ldha) using RNA from MSCs from 1-month-old Prx1-Cre; IFT20f/f mice and controls as indicated. (C) Representative image of immunofluorescence staining for Glut1 in tibiae from Prx1-Cre; IFT20f/f mice and age-mated controls as indicated. Scale bars, 75 μm. N = 5. (D) Representative immunohistochemistry image of Glut1 in tibiae from 1-month-old Prx1-Cre; IFT20f/f mice and controls as indicated. Scale bars, 75 μm. N = 5. Relative intensity of Glut1 was measured as indicated. (E) mRNA levels of Glut1-4 in MSCs from IFT20f/f mice after treatment with Ad-GFP or Ad-Cre for 48 h. (F, G) Glucose consumption and lactate production after treatment of Ad-GFP or Ad-Cre for 48 h as indicated. (H) ATP production. (I) 2-NBDG uptake. After incubation with 100 μM 2-NBDG of 8 h, the glucose uptake was determined by a fluorescence microscope at 485/540 nm. (J) Glucose consumption after treatment of Ad-GFP or Ad-Cre with/without the glycolysis inhibitor 2-DG for 48 h as indicated. (K) Visualization of 2-NBDG uptake in tibiae after injection of 2-NBDG for 45 min. N = 3. (L–N) The glucose consumption (L), lactate production (M), and ATP level (N) were identified after overexpression of IFT20 in MSCs for 48 h. Error bars were the means ± SEM from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.