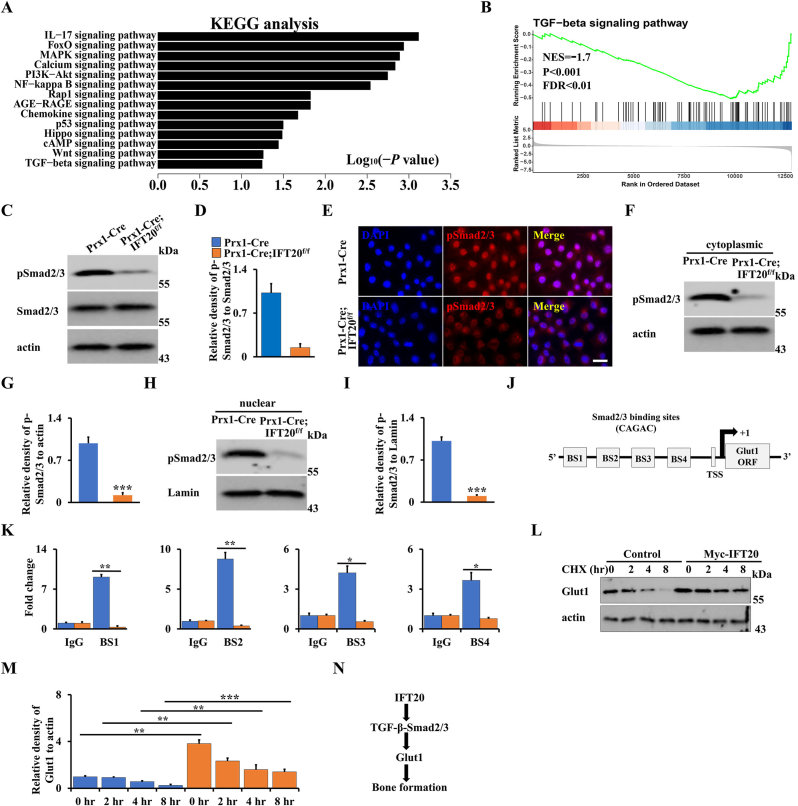
Fig. 7.
IFT20 promotes Glut1 expression through TGF-β-Smad2/3 signaling. (A) KEGG analysis of significant change of genes after loss of IFT20 in MSCs. (B) GSEA analysis showed a significant decrease of TGF-β signaling after loss of IFT20 in MSCs as indicated. NES, normalized enrichment score. FDR, false discovery rate. (C, D) The analysis of Western blot and the quantification as shown. N = 3. (E) Representative fluorescence image of pSmad2/3 as shown. Scale bars, 10 μm. (F–I) Nuclear and cytoplasmatic Western blot analysis as shown. N = 3. (J) Schematic diagram of Smad2/3 DNA binding motifs in the Glut1 promoter. BS, binding site. TSS, transcription start site. (K) ChIP assay. Co-occupation of Smad2/3 in the Glut1 promoter as indicated. (L, M) After transfection of Myc-IFT20 or empty vector for 24 h in MSCs, the MSCs were treated with 50 μg/mL CHX for different times as indicated, and then the Glut1 levels were identified by Western blot (L). The quantification was analyzed at (M). N = 3. (N) Proposed mechanism of IFT20 governs mesenchymal stem cell fate through TGF-β-Smad2/3-Glut1 axis. IFT20 in MSCs favors to osteogenesis instead of adipogenesis by maintaining the expression and stability of TGF-β-Smad2/3-mediated Glut1 and enhancing its mediated glucose metabolism. Error bars were the means ± SEM from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. ***P < 0.001.