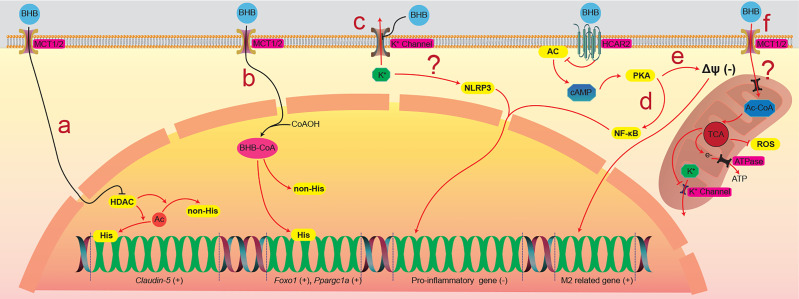
Figure 2.
The physiological processes that BHB direct regulates. (A) BHB across the plasma membrane enters the nucleus and inhibits HDACs, which participate in the deacetylation of histone and nonhistone proteins, resulting in the increased expression of the claudin-5 gene in the cardiovascular endothelial cells. (B) BHB that enters the nucleus was activated into acetylated BHB and then β-hydroxybutyrates histone and nonhistone proteins, resulting in the increased expression of Foxo1 and Ppargc1a gene in the CD8+ T cells. (C) BHB holds back the K+ channel in the plasma membrane, which maintains the cytoplasmic K+ concentration and inhibits the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. BHB activates HCAR2, a seven-transmembrane G-protein coupled receptor of the Gi family, and inhibits the activity of the AC/cAMP/PKA signaling pathway. (D) the inhibition of the AC/cAMP/PKA signaling pathway decreases the mitochondrial membrane potential and promotes the transcription of M2-related genes in intrahepatic macrophages. (E) the inhibition of the AC/cAMP/PKA signaling pathway also inhibits the activation of NF-κB, consequently inhibiting the expression of pro-inflammatory genes in primary rat microglial cells. (F) the oxidation of BHB in the mitochondrion closes the channel proteins in the mitochondrial intima, which inhibits the outflow of ROS. BHB, β-hydroxybutyrate; BHBtion, β-hydroxybutyration; MCT, monocarboxylate transporter; HCAR2, hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2; HDACs, histone deacetylases; Ac, acetyl group; His/non-His, histone/nonhistone proteins; AC, adenylate cyclase; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PKA, protein kinase A; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; Ac-CoA, acetyl coenzyme A; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; ROS, reactive oxygen species; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; ATPase, ATP synthase.