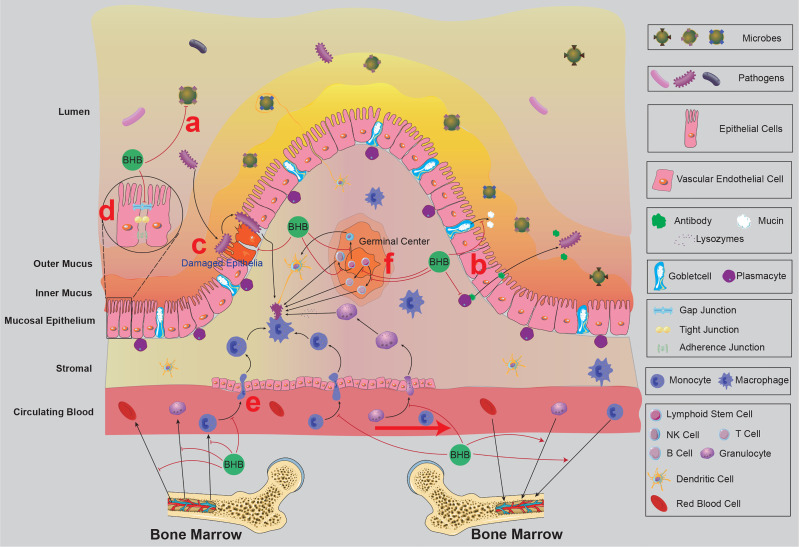
Figure 3.
The mucosal immunity of the intestine and the possible effects of BHB on intestinal mucosal immunity. BRC and circulating immune cells from bone marrow circulate in the blood and lymphatic system and then return to the bone marrow. BHB was found to accelerate the homing process of circulating naïve B cells, decrease the expression of CXCL13 (a chemokine that recruits naïve B cells) in the intestinal vascular endothelial cells and stromal cells, and increase the expression of adhesion proteins between vascular endothelial cells, indicating BHB might reduce the chance of circulating immune cells infiltrating into the intestinal mucosa. The germinal centre in the intestine tissue contains multiple kinds of follicular lymphocytes, which are released into the stromal participating in the immune defence process. BHB was found to inhibit the proliferation and differentiation of primary follicular lymphocytes, indicating BHB might reduce the number of follicular lymphocytes in the stromal. There are massive microbes on the surface of the small intestinal mucosa, which prevents the colonization of pathogens (Microbiota Barrier). BHB was found to inhibit the growth of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus in the intestine and alter the microflora community of the nasopharynx, indicating BHB affects the microbiota barrier of mucosal. Covering the surface of mucosal epithelium, a layer of mucus consists of kinds of chemical components (Chemical Barrier), including mucins secreted by goblet cells, antibacterial peptides secreted by epithelial types of cells, and sIgA secreted by plasma cells, et al. BHB was found to affect the thickness and viscosity of the mucosal layer, indicating BHB might affect the secretory function of these secretory cells. The mucosal epithelial cells are woven into a dense network by tight junctions and intermediate junctions, including occlaudin, claudin, E-cadherin, Ep-CAM, et al. This network prevents pathogens from invading the mucosal tissue and resulting in infection (Physical Barrier). BHB affects the expression of adhesion proteins between vascular endothelial cells, indicating that it might also affect the physical barrier of mucosal epithelium. Macrophages, DCs and other immune cells play important roles in recognizing and eliminating the invaded pathogens. BHB was found to decrease the pro-inflammatory activities of granulocytes and macrophages, indicating that BHB might also affect the activities of immune cells in the infected mucosal tissues. BRC, blood-red cell; BHB, β-hydroxybutyrate; sIgA, secretory immunoglobulin; E-cadherin A, epithelial cadherin; Ep-CAM, epithelial cell adhesion molecule; DCs, dendritic cells.