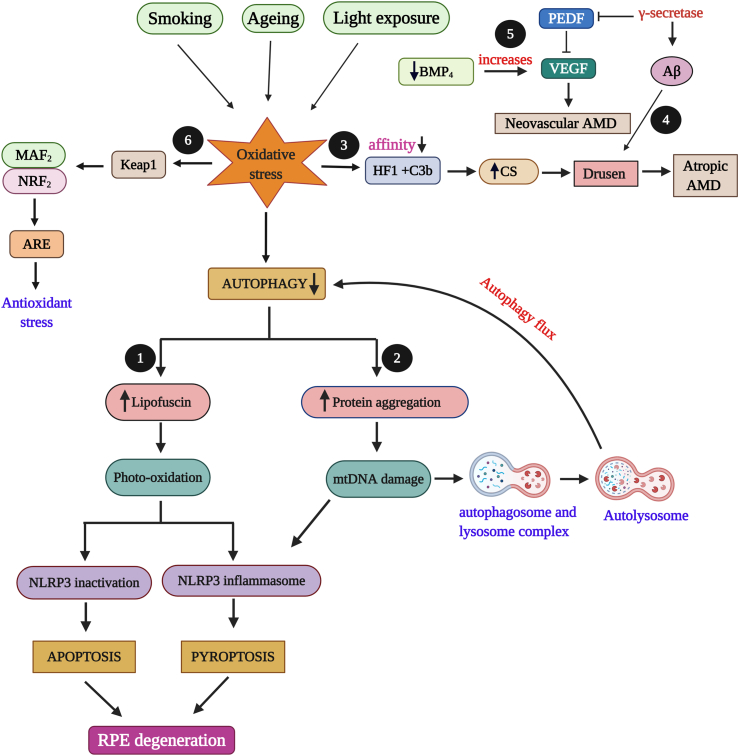
Figure 1.
Oxidative stress (OS) effects in RPE degeneration. External factors (ageing, smoking, light) induce increased oxidative stress (OS) that leads to decreased autophagy. The following are the possible and reported effects of OS in RPE. 1) Decreased autophagy causes an increase in lipofusin that result in apoptosis and pyroptosis which leads to age related macular degeneration (AMD). 2) Increase in protein degradation and aggregation leads to mitochondrial damage and autophagy flux. 3) OS lessens the affinity between compliment factor H gene (HF1) and C3b which increases the activation on complement system (CS) that results in Drusen formation with atropic AMD. 4) γ-secretase involves in amyloid-β (Aβ) formation which results in Drusen formation. 5) γ-secretase damages and inhibits pigment epithelium derived factor (PEDF) which in turn irregulates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) activity that leads to neovascular AMD. Decrease in bone morphogenic protein 4 (BMP4) increases VEGF and results in neovascular AMD. 6) OS alters the structure of Keap1 that leads to Nrf2 transition to the nucleus, were it interacts with MAF2 proteins and binds to antioxidant response elements (ARE) which results in antioxidant stress.