FIGURE 3.
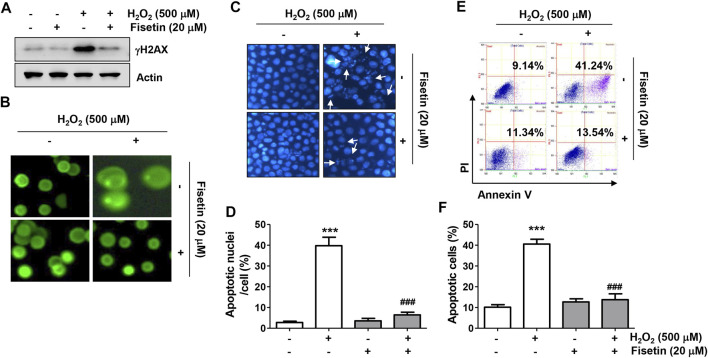
Fisetin protected ARPE-19 cells against H2O2-induced DNA damage and apoptosis. Cells were stimulated with or without 20 μM fisetin for 1 h and then treated with 500 μM H2O2 for another 24 h. (A) Levels of total p-γH2AX and actin were determined by immunoblotting using cell lysates. (B) Comet assay was performed to analyze DNA damage. Representative immunofluorescence microscopic images are shown. H2O2-induced increases in p-γH2AX expression and comet tail formation were apparently alleviated pretreatment of fisetin. (C,D) Cells were stained with DAPI for nuclear morphological observation under a fluorescence microscope for detection of apoptosis. (C) Representative images of DAPI-stained nuclei are shown. (D) Quantification results of nuclei with apoptotic cells are shown in a graph. H2O2-exposed cells displayed typical apoptotic properties such as nuclear shrinkage and fragmentation, whereas H2O2-mediated morphological changes were markedly restored by fisetin pretreatment. (E,F) After treatment, flow cytometry with annexin V/PI dual staining was performed. Representative histograms (E) and quantitative analysis (F) are shown. Pretreatment of fisetin significantly reduced the increased frequency of apoptotic cells following H2O2. (D,F) The graph represents the mean with SD (n = 3, *** p ˂ 0.001, compared with the control group; ### p ˂ 0.001 compared with H2O2 treatment group).