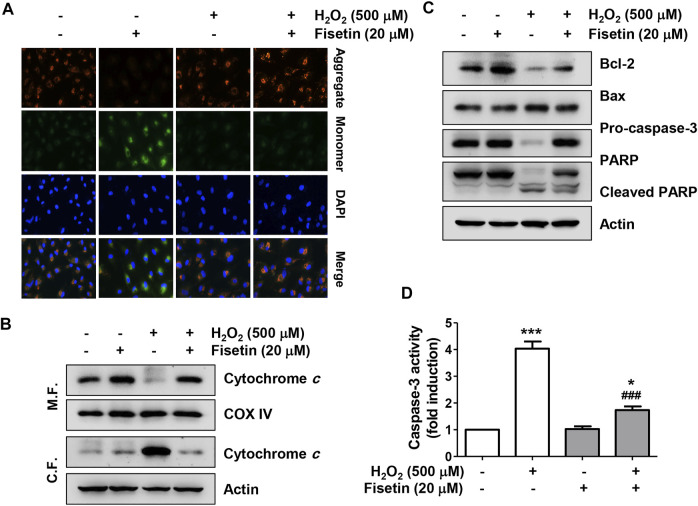
FIGURE 4.
Fisetin ameliorated H2O2-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in ARPE-19 cells. Cells were treated with or without 20 μM fisetin for 1 h and then treated with 0.5 mM H2O2 for 24 h (A) mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) was examined by the change in JC-1-derived fluorescence. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). After staining, representative images of JC-1 aggregates (red, representing high potential) and monomers (green, representing low potential) of cells of each treatment group were captured using a fluorescence microscope. Pretreatment of fisetin reversed down-regulation of the ratio of JC-1 aggregates/monomers following H2O2-induced MMP depolarization. (B) To evaluate the expression and localization of cytochrome c, mitochondrial (M. F.) and cytoplasmic (C. F.) fractions were isolated from cells and assessed by Western blot analysis. cytochrome c was released from the mitochondria to the cytoplasm by H2O2, while pretreatment of fisetin was reversed H2O2-induced cytochrome c release. (C) Changes in the expression of Bcl-2, Bax, caspase-3, and PARP were confirmed using the extracted total proteins. (D) Caspase-3 activity was determined using a commercially available kit, and the concentration of p-nitroanilide released by activated caspase-3 was presented as a relative value compared to the control. H2O2 down-regulated the expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein while up-regulating the expression of pro-apoptotic Bax, and induced the activation of caspase-3 and degradation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). However, pretreatment of fisetin clearly reversed these H2O2-mediated alterations. All bar graphs represent mean ± SD (n = 3, * p ˂ 0.05, and *** p ˂ 0.001 compared with control group; ### p ˂ 0.01 compared with H2O2 treatment group).