Figure 4.
Validation of VTK vectors functionality
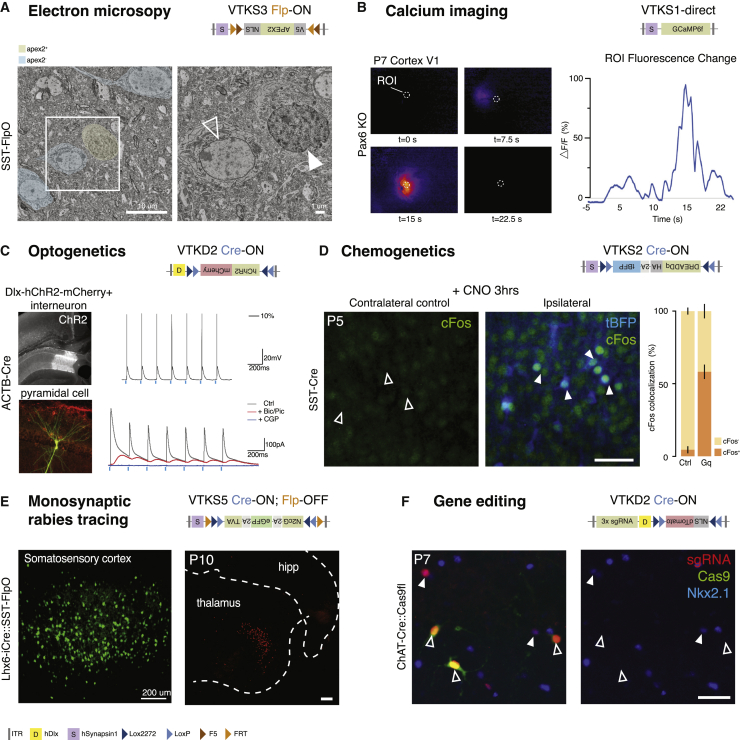
(A) VTKS3-NLS-APEX2-V5 injected into the somatosensory cortex of SST-FlpO mice allowed for the labeling of sparse populations of nuclei. SST cells with an APEX2-positive nucleus are labeled in yellow (full arrow) and negative ones in blue (empty arrow). Scale bar: 10 μm (left) and 1 μm (right).
(B) Calcium events from VTKS1-GCaMP6f-infected cells were found in the visual cortex of Pax6 knockout (KO) mice. Waves of spontaneous infected cell activity were detected. Graph represents the difference in fluorescence (ΔF/F%) detected in the region of interest (ROI) over time.
(C) Top, cells infected by VTKD2-hChR2-mCherry in dorsal hippocampus of ACTB-Cre mice show depolarization upon blue-light stimulation; bottom, ChR2-mCherry-negative neighboring pyramidal cells receive light-evoked inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs). IPSCs are blocked by bicuculline (Bic)/picrotoxin (PIc) and CGP55845 (CGP) and GABAa and GABAb receptor antagonists, respectively.
(D) VTKS2-driven Dreadd-Gq (tBFP) triggers the expression of the immediate-early gene, cFos, after 3 h of CNO activation compared with the control on the contralateral side (Ctrl: 4.47% ± 2.4%, N = 3; after CNO: 58.21% ± 5.19%, N = 6; data are shown as mean ± SEM). Full arrows: cFos + tBFP colocalization upon activation. Empty arrows: absence of cFos in Ctrl. Scale bar: 50 μm.
(E) Left, VTKS5-rabies helpers (N2cG-eGFP-TVA) are injected in the somatosensory cortex of Lhx6-iCre::SST-FlpO animals. Right, example retrograde labeling tracing found at the thalamus level after secondary rabies infection of helper+ cells. Scale bar: 200 μm (left and right).
(F) Three CRISPR guides (sgRNA) targeting Nkx2.1 gene are inserted in VTKD2-NLSdTomato and injected in ChAT-Cre mice::Floxed-Cas9 mice. sgRNA (red) in Cas9-positive (green) cells suppressed Nkx2.1 expression (blue, empty arrows). Cells without colocalization still express Nkx2.1 (full arrows). Scale bar: 50 μm.