Figure 2.
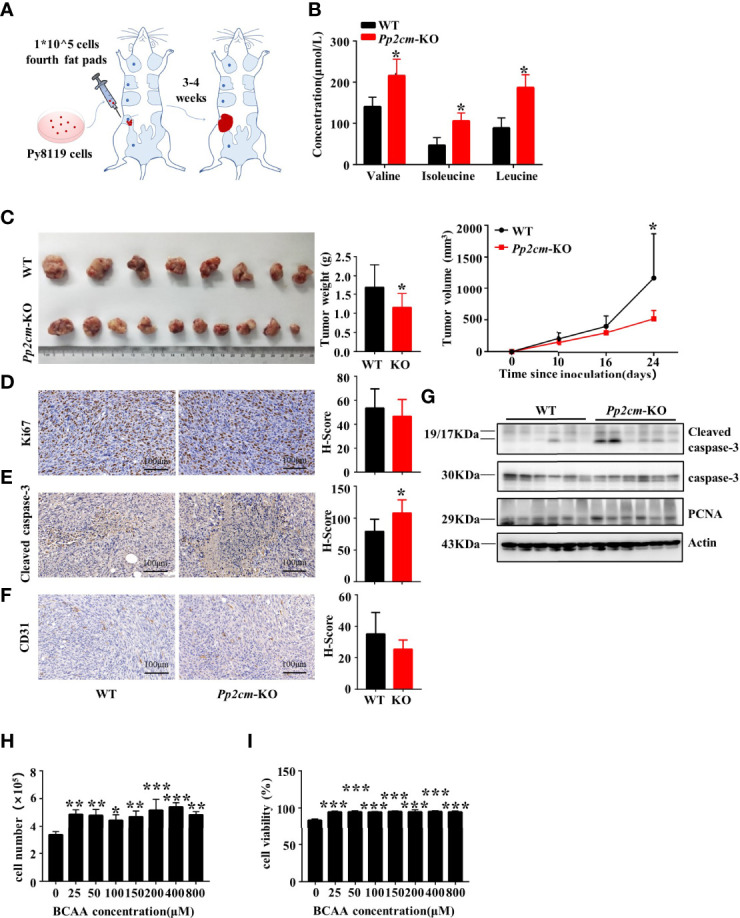
Elevated BCAA inhibits orthotopic tumor growth of breast cancer. (A) The orthotopic allograft model. (B) The serum BCAA concentration of tumor-bearing mice after 6 hours of fasting. Mean ± SD, *p < 0.05, Student’s t-test. (C) The tumor-bearing Pp2cm-WT/KO mice were euthanized at 21days and tumor were harvested (Pp2cm-WT, n=8; Pp2cm-KO, n=10). Tumor weight was measured at the end of the experiment and tumor volume was calculated using the following formula: tumor volume (cubic millimeters (mm3)) = 0.5× (length×width2). Mean ± SD, *p < 0.05, Student’s t-test. (D) Proliferation marker Ki67, (E) apoptosis marker Cleaved caspase-3, and (F) angiogenesis marker CD31 expression was analyzed by immunohistochemistry. Mean ± SD, *p < 0.05, Student’s t-test. (G) Western blot was used to analyze the protein expression of Cleaved caspase-3, caspase-3 and PCNA (n=6 in each group). (H-I) Py8119 cell number and viability assay using Trypan blue exclusion test after treatment with different concentrations of BCAA for 48 hours. Cell viability was calculated as the number of viable cells divided by the total number of cells. The BCAA gradient medium was prepared with 8000μM BCAA storage solution and custom BCAA-free DMEM. The storage solution was prepared from BCAA powder. BCAA treated groups (25μM, 50μM, 100μM, 200μM, 400μM, 800μM) were compared with the 0μM BCAA group. Mean ± SD, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ANOVA.
