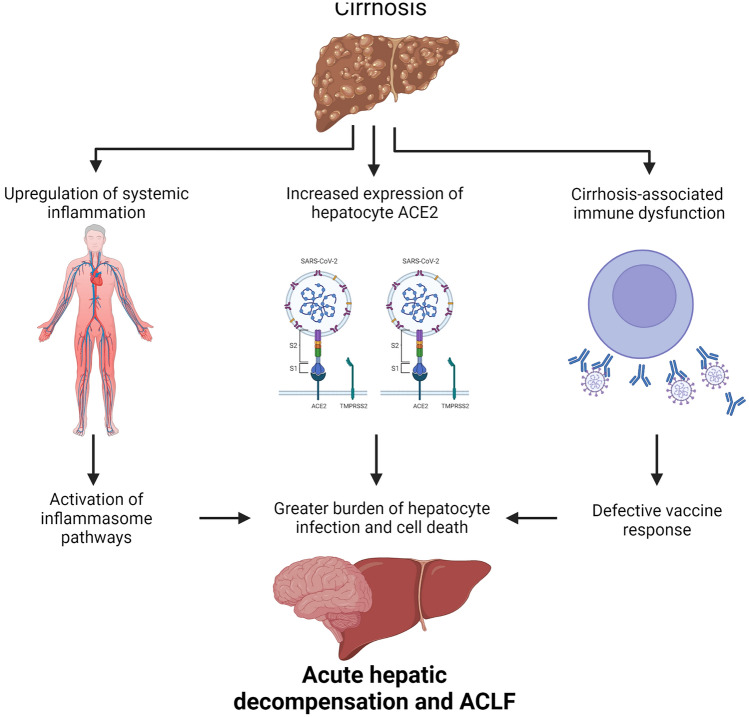
Fig. 2.
Patients with cirrhosis are at greater risk of developing acute hepatic decompensation upon SARS-CoV-2 infection, since they display weaker response to the vaccine resulting in lower levels of circulating antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and also have increased expression of ACE2 on the hepatocyte membrane. ACE2 is not typically expressed on the surface of healthy hepatocytes but has elevated expression in cirrhosis permitting entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the cell. Cirrhosis is also associated with low-levels of circulating gut-derived bacterial products, which predispose to systemic inflammation and upregulation of inflammasome pathways. This results in sensitisation of hepatocytes to SARS-CoV-2 infection and subsequent pro-inflammatory cell death and immune responses