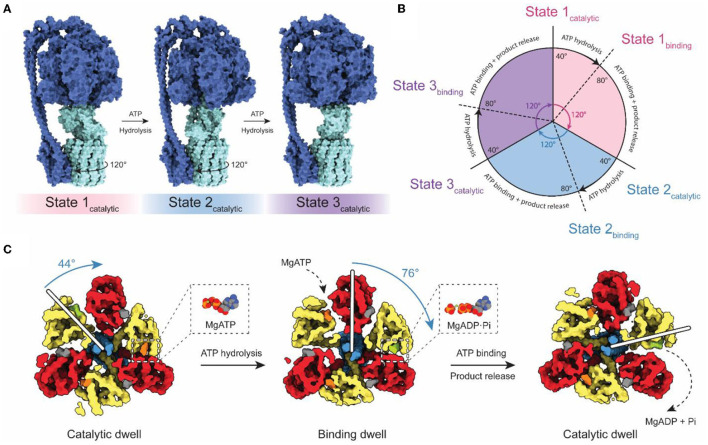
Figure 2.
Rotary catalytic mechanism of ATP synthase. (A) Atomic model of Bacillus PS3 ATP synthase showing the three main rotational states (PDB: 6N2Y, 6N30, and 6N2Z) (Guo et al., 2019). The light blue parts of the complex rotate relative to the dark blue parts. The direction of rotation during ATP hydrolysis is indicated. (B) Diagram of the catalytic cycle of the F1 region during ATP hydrolysis. (C) Structures of the Bacillus PS3 F1 complex catalytic substeps (PDB: 7L1R and 7L1Q) (Sobti et al., 2021). White bars represent the angle of the γ subunit. ATP, ADP, and non-catalytic nucleotides are colored orange, green, and dark gray, respectively. Based on Sobti et al. (2021).