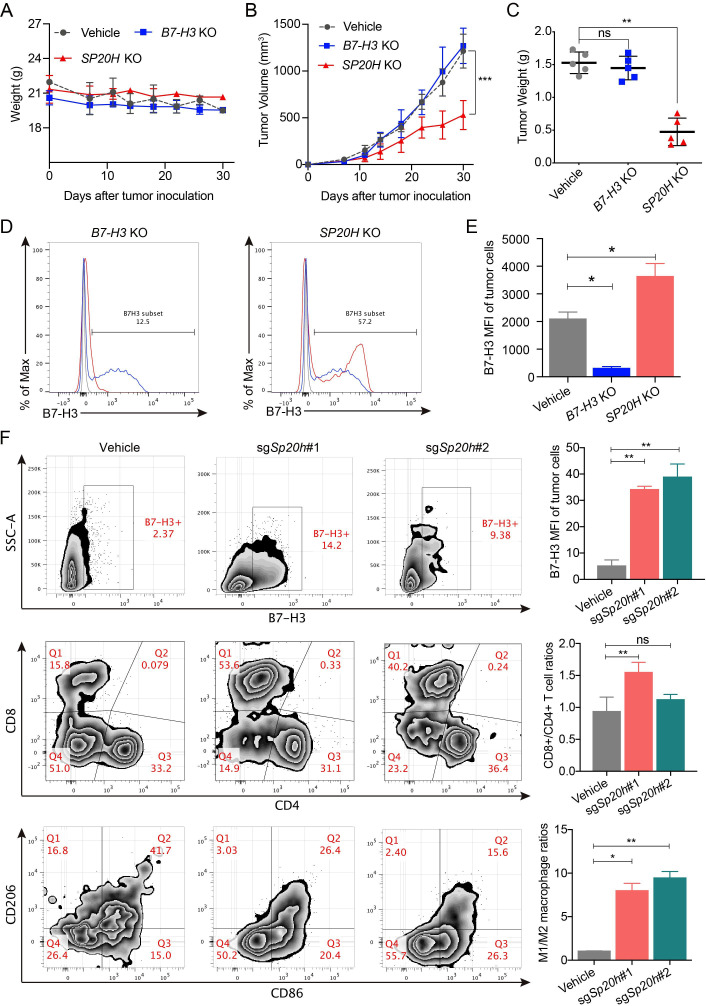
Figure 5.
SP20H inactivation represses tumor growth in vivo and increases populations of proinflammation T cells and macrophages. (A–B) Body weight changes and subcutaneous tumor growth curve of SK-OV-3 vehicle, SP20H-KO, or B7-H3-KO cells in NOD-SCID mice were plotted (n=5; ***p<0.001). (C) Tumors were excised and weighed 30 days after tumor challenge (n=5; **p<0.01; ns, no significant). (D) Analysis of surface B7-H3 expressions on B7-H3-deficient or SP20H-deficient tumor cells from SK-OV-3 tumor-bearing NOD-SCID mice by flow cytometry. (E) Statistical analysis of corresponding MFI of B7-H3 in (D); *p<0.05. (F) Flow cytometry analysis of surface B7-H3 expression of tumor cells(upper), frequencies of tumor-infiltrating T cells (middle) and macrophages (lower) in control or sgSp20h-4T1 tumor-bearing BALB/c mice. Tumor cells were gated on CD45− CD11B− live cells; the CD45+ CD3+ live cells were divided into CD4+ and CD8+ T cells; the CD45+ CD11B+ F4_80+ live cells were divided into M1-like (CD86+ CD206−) and M2-like (CD86− CD206+) macrophages. Data shown are representative results. The p values were determined by a two-tailed paired Student’s t-test (n=3; *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ns, no significant).