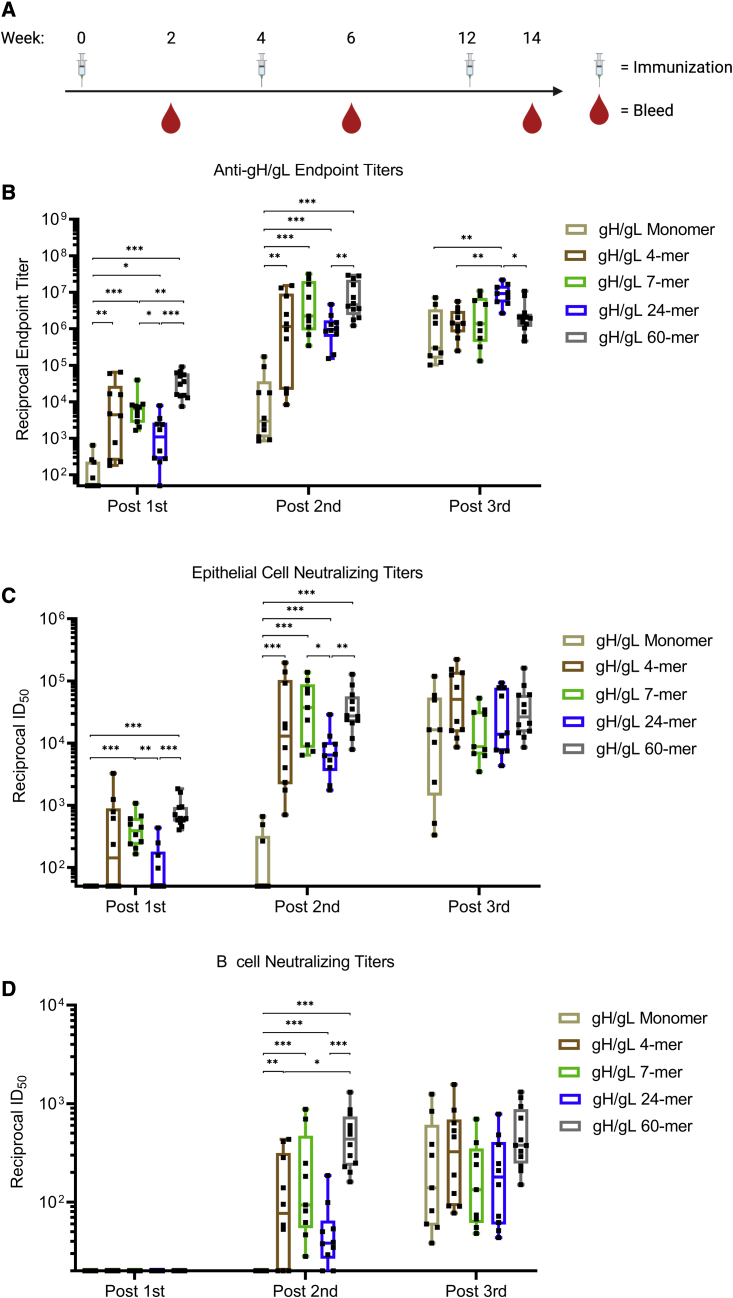
Figure 2.
Immunogenicity of gH/gL nanoparticles
(A) C57BL/6 mice (n = 10 mice for gH/gL monomer and 4-, 7-, and 24-mer, and n = 12 for gH/gL 60-mer) were immunized with monomeric gH/gL or multimeric gH/gL nanoparticles at weeks 0, 4, and 12. Blood was collected 2 weeks after each immunization.
(B) Endpoint plasma binding titers to gH/gL were measured by ELISA. Each dot represents the reciprocal endpoint titer for an individual mouse measured in duplicate. Box and whisker plots represent the minimum, 25th percentile, median, 75th percentile, and maximum values.
(C and D) The ability of plasma from individual mice to neutralize EBV infection of epithelial cells (C) or B cells (D). Each dot represents the reciprocal half-maximal inhibitory dilution (ID50) titer of an individual mouse. Plasma that did not achieve 50% neutralization at the lowest dilution tested (1:20) was assigned a value of 10. Box and whisker plots represent the minimum, 25th percentile, median, 75th percentile, and maximum values. Significant differences in B–D were determined using Mann-Whitney tests with Holm-adjusted p values (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001).
See also Figures S1 and S2.