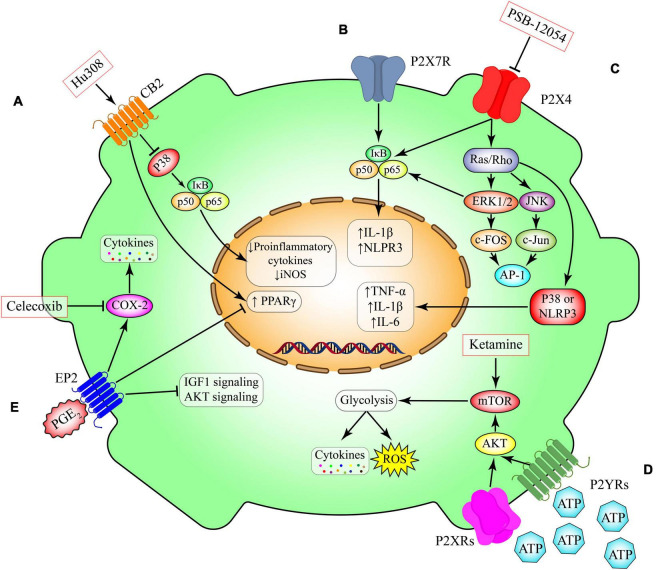
FIGURE 3.
Metabolic pathways in microglia. (A) Activation of CB2 receptors that are expressed in non-neural cells including microglia promotes anti-inflammatory cascades through inhibition of NFκB or induction of anti-inflammatory transcriptional factor such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ). This pathway can be induced by Hu308. (B) P2X7 receptor activation, induces the canonical pro-inflammatory transcriptional factors such as NFκB and subsequent production of inflammatory mediators such as IL-1 beta and NLPR3. (C) Activation of ligand gated ion channel P2X4 triggers the switching on two canonical pathways including NFκB and Ras/ERK/JNK. These proteins induce the production of several cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-beta and IL-6. This pathway can be inhibited by PSB-12054. (D) Induction of the G-protein coupled receptors P2YRs have essential roles in modulating the expression of metabolic pathways such as mTOR and their downstream glucose metabolism. The induction of glycolysis through mTOR has been implicated in production of several cytokines and chemokines. Ketamine triggers the mTOR pathways leading to induction of glycolysis. (E) Prostaglandin E2 (PGE 2) is a lipid mediator derived from the fatty acid arachidonic acid. Its interaction with the microglial G-protein coupled receptor EP2 induces the activity of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inhibits several intracellular pathways including PPAR-γ, AKT and IGF1. Celecoxib is s selective COX-2 inhibitor. CB2, cannabinoid type 2 (CB2) receptor; P2X4, P2X purinoceptor 4; P2X7, P2X purinoceptor 7; P2YR, purinergic receptor P2Y; EP2, prostaglandin E2 receptor 2; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; IGF1, insulin-like growth factor 1; AKT, RAC(Rho family)-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; IL-1β, interleukin 1 beta; IL-6, interleukin 6; PPAR-γ, peroxisome proliferator- activated receptor-gamma; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; AP-1, activator protein 1; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinases; NLRP3, NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; ERK, extracellular-signal-regulated-kinase; IκB, nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor; ROS, reactive oxygen species.