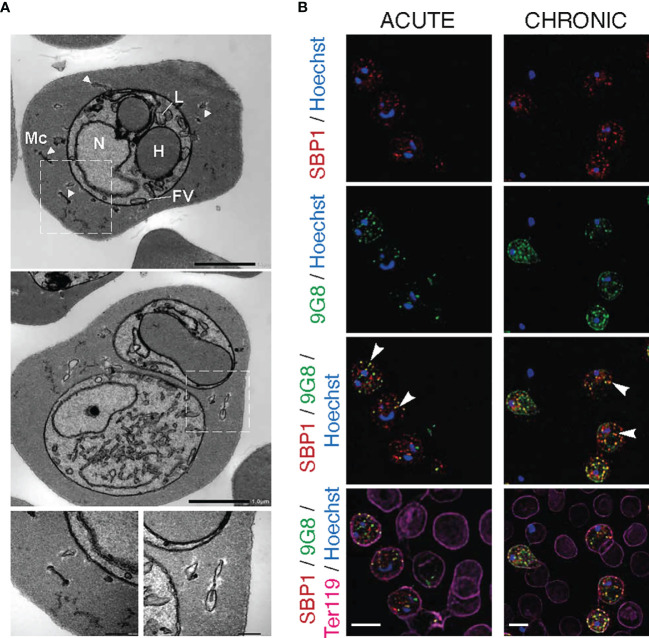
Figure 4.
Maurer’s clefts-like structures in P. c. chabaudi AS infected erythrocytes. (A) Transmission electron micrographs of a P. chabaudi MT acute phase trophozoite, inside a mouse erythrocyte. The white arrowheads indicate Maurer’s clefts within the iRBC cytosol. Insets show sections of the areas highlighted. Scale bar length corresponds to 1 μm and 0.2 μm in insets. FV, Food Vacuole; H, Haemoglobin Filled Compartment; L, Lipid Droplets; Mc, Maurer’s clefts; N, Nucleus. (B) Immunofluorescence assays of MT acute- (left panels) and chronic- (right panels) phase WT P. chabaudi parasites at the late trophozoite-stage. Blood was isolated from C57Bl/6 RAG1-/- mice. Parasites were primarily stained with the anti-PbSBP1 antibody (De Niz et al., 2016) (red) and then with the anti-clone 6 (9G8) monoclonal antibody (green). The RBC surface membrane was stained with the anti-Ter119 monoclonal antibody (magenta), and parasite nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). The white arrowheads indicate co-localisation of SBP1 with 9G8. Images were taken from confocal sections of acetone:methanol fixed parasites at X630 magnification. Scale bar length corresponds to 5 μm.