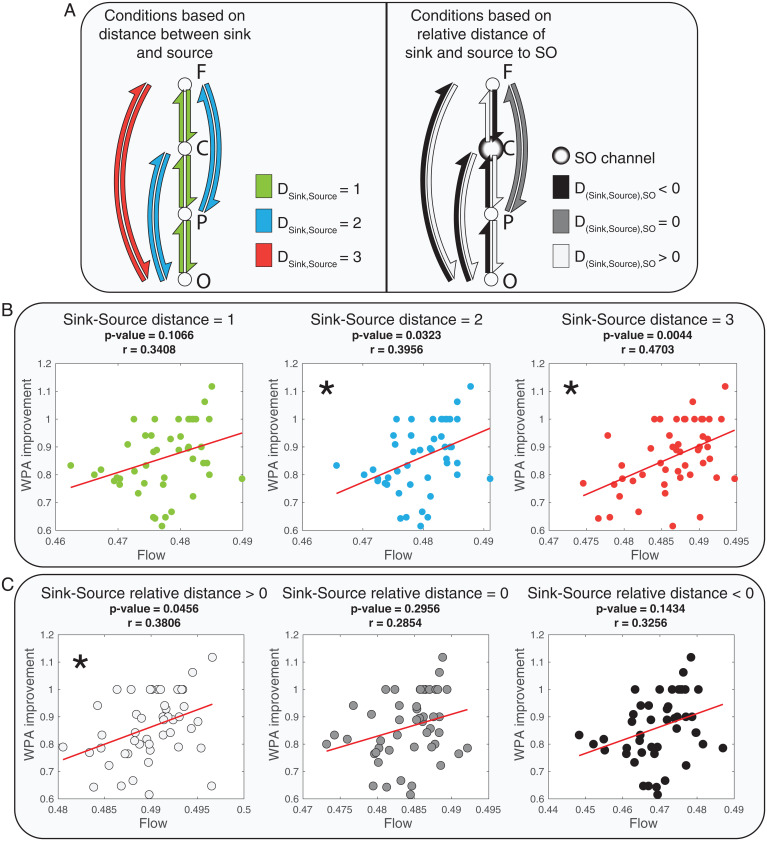
Fig. 4.
Linear relationships between flow and WPA improvement based on different distances between sinks and sources and relative distances of sinks and sources to SO channels. The asterisks mark significant linear relationships (with P values adjusted to Bonferroni correction). (A) A representation of the three conditions of distances between sinks and sources (Left) and an example of three possible conditions of relative distances of sources and sinks to the SO channel (Right, for SO channel at Cz). F, C, P and O represent frontal, central, parietal and occipital regions respectively. Left: Each color represents pairs of sinks and sources of information flow with equal distances. Right: Graph shows an example of relative distance when the SO channel is in Cz. The relative distance is greater than 0 when the source is closer to the SO channel than the sink and smaller than zero when the sink is closer to the SO channel than the source . (B) Correlation and regression tests of the relation between flow and WPA improvement for three conditions of distance between sources and sinks (). (C) Correlation and regression tests of the relation between flow and WPA improvement for three conditions of relative distance between sources and sinks to the SO channel.