FIGURE 1.
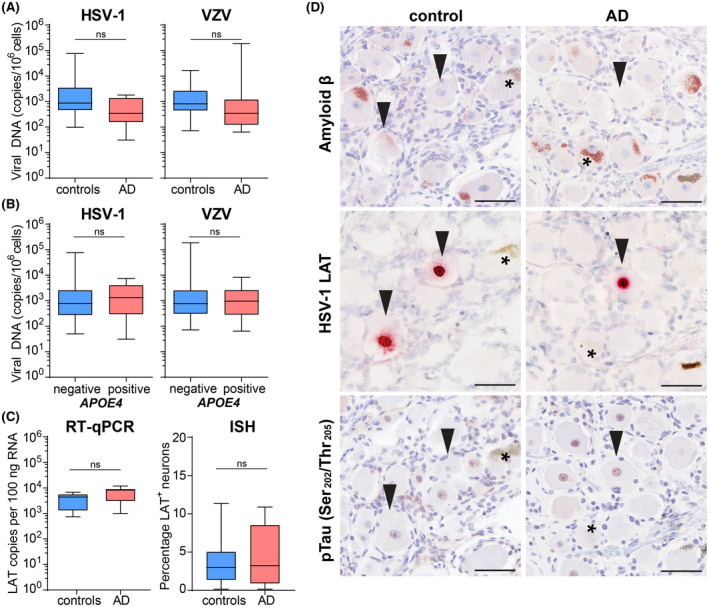
HSV‐1 infection is not associated with aberrant Aβ or pTau expression in latently infected human trigeminal ganglia (TG) neurons. (A, B) HSV‐1‐ and VZV‐specific qPCR was performed on DNA extracted from the TG of Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients and control subjects, stratified on disease status (A; 20 controls and 10 AD patients) or APOE4 allele carrier status (B; HSV‐1: 22 APOE4‐negative and 8 APOE4‐positive individuals; VZV: 24 APOE4‐negative and 13 APOE4‐positive individuals). Horizontal line: median. (C) Detection of LAT RNA by RT‐qPCR (7 AD patients and 7 controls) and ISH (11 controls and 5 AD patients; 3 sections per donor analyzed) in human TG from AD patients and control subjects. (D) Sequential TG sections from AD (n = 4) and control (n = 6) subjects were stained for amyloid β protein, HSV‐1 latency‐associated transcript (LAT) RNA and phosphorylated Tau protein (pTau; Ser202/Thr205) by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and RNA in situ hybridization (ISH). Arrowheads indicate LAT‐positive neurons and asterisks indicate lipofuscin granules. Scale bar: 50 µm
