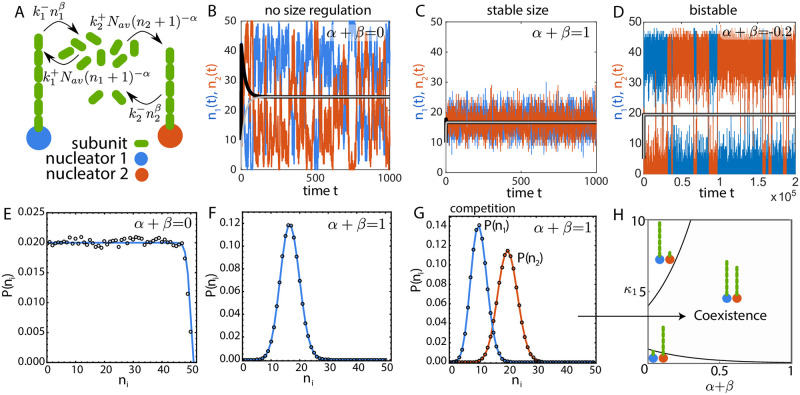
Fig 1. Size regulation of two structures grown from a shared subunit pool.
(A) Schematic of two filaments growing from a shared pool of monomers where the assembly and disassembly rates depend on their individual size. (B-D) Size dynamics of two identical filaments (κ1 = κ2 = κ = 1 for B and C) obtained from stochastic simulations in three distinct growth regimes: (B) α + β = 0 (for deterministic solution α = −1 and β = 1), (C) α + β = 1 (α = 0, β = 1) and (D) α + β = −0.2, κ = 0.0022 (α = −0.2, β = 0). The black (n1) and gray (n2) solid lines are the deterministic solutions to the rate equations of size. The deterministic solution correctly captures the mean size dynamics for α + β = 1, but fails to predict the essential features of size dynamics in the two other cases. (E-F) Size distribution of two identical structures for (E) α + β = 0 and (F) α + β = 1. Open circles represent solution from stochastic simulation and the solid line represents the analytical solution to the chemical master equation. (G) Size distribution for two competing structures with α + β = 1 and κ1 = 2κ2 = 1, obtained from analytical solution to the master equation (solid line) and stochastic simulations (open circles). (H) Phase diagram showing the co-existence of two competing structures over a broad range of parameter space in the model, with κ2 = 2. Coexistence phase is defined as both structures having mean size larger than one subunit. For all results in (A-H) V = 1 and N = 50.