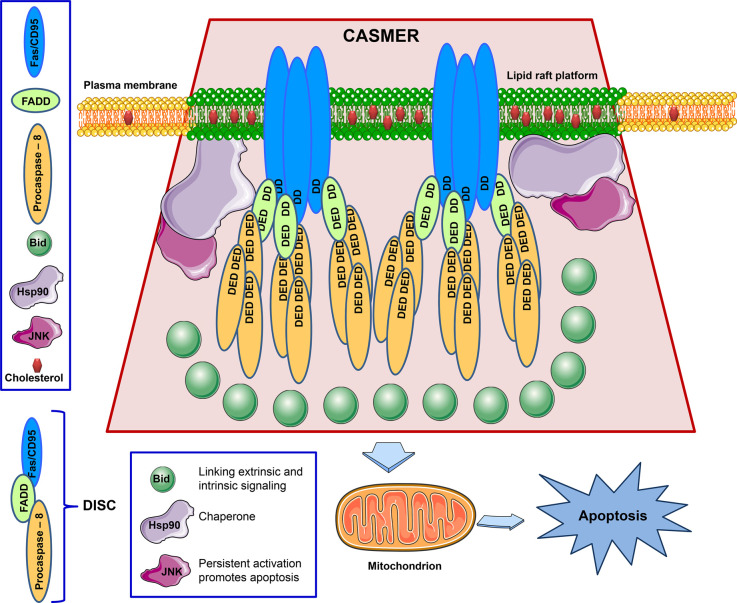
Figure 1. The concept of CASMER.
Apoptotic signaling molecules, including Fas/CD95, FADD and procaspase-8, forming the DISC, are brought together in close proximity, through homotypic interactions of DD and DED domains between the DISC constituents, in large cholesterol-enriched lipid raft platforms (highlighted in green) as a result of raft clustering. This leads eventually to a high concentration of procaspase-8 molecules that favors its autoproteolytic activation. Additional downstream signaling molecules, such as Bid, can also be recruited to the CASMER, acting as a bridge between death receptor extrinsic apoptotic signaling and mitochondrial-dependent intrinsic apoptotic signaling, thus potentiating apoptosis. JNK could also be translocated into CASMERs, and persistent JNK activation potentiates apoptosis. The activity of JNK can be protected by chaperones, such as Hsp90, that when redistributed into rafts replace their classical client proteins with other proteins predominant in these proapoptotic rafts. The formation of the supramolecular entity CASMER highly facilitates protein–protein interaction and cross-talk signaling, and eventually favors the generation and amplification of different apoptotic signals, including caspase activation- and mitochondria-mediated processes, that lead to the same outcome, viz., the trigger of apoptosis. Thus, CASMERs act as linchpins from which the apoptotic response is highly amplified. See text for further details.