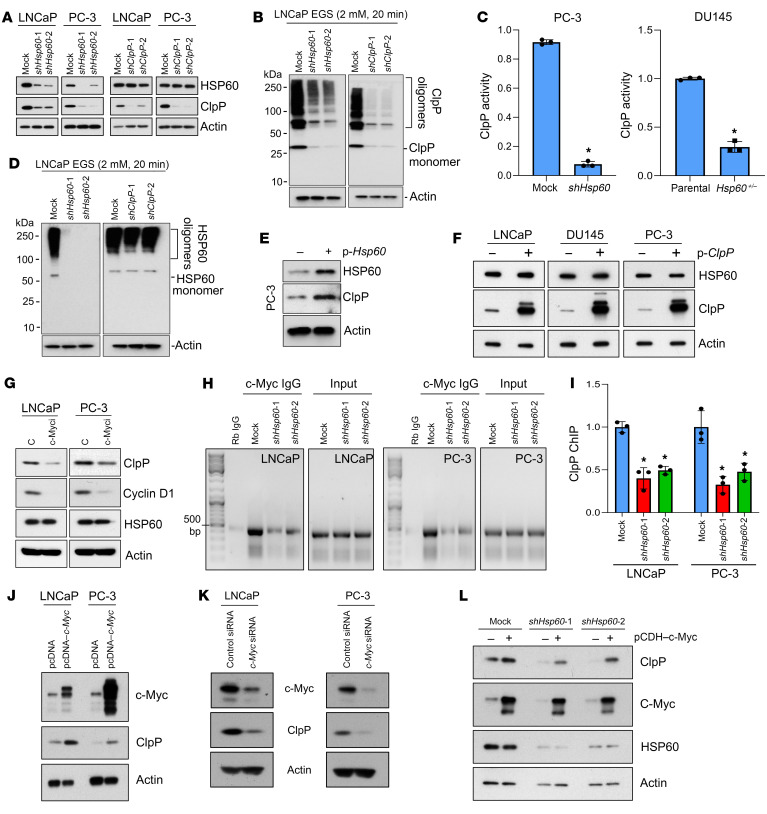
Figure 1. HSP60 regulates ClpP expression and function via c-Myc but not vice versa.
(A) Hsp60- and ClpP-silenced LNCaP and PC-3 cells were analyzed for HSP60 and ClpP expression. (B) Hsp60-and ClpP-silenced LNCaP cells were crosslinked with ethylene glycol bis(succinimidyl succinate) (EGS). Protein samples were resolved in an SDS-PAGE gel and probed with an anti-ClpP antibody to analyze its oligomerization status. (C) Enzymatic activity of ClpP was assayed from mitochondrial pellets isolated from Hsp60-silenced PC-3 cells and Hsp60+/– DU145 cells. Data are presented as fold change compared to respective controls. (D) Hsp60- and ClpP-silenced LNCaP cells were crosslinked with EGS. Protein samples were resolved in an SDS-PAGE gel and probed with an anti-HSP60 antibody to analyze its oligomerization status. (E) HSP60 was overexpressed in PC-3 cells and analyzed for ClpP expression. (F) ClpP was overexpressed in LNCaP, DU145, and PC-3 cells and analyzed for HSP60 expression. (G) LNCaP and PC-3 cells were untreated (C) or treated with c-Myc inhibitor (c-Myci, 10058-F4, 50 μM) for 24 hours. Whole-cell lysates (WCLs) were prepared and analyzed for cyclin D1, ClpP, and HSP60 expression. (H) Efficiency of c-Myc binding to the ClpP promoter in Hsp60-silenced LNCaP and PC-3 cells was determined using a chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay. (I) Quantitation of the data shown in H, represented as fold change compared to mock cells. (J) c-Myc was overexpressed in LNCaP and PC-3 cells and analyzed for ClpP expression. (K) c-Myc was silenced in LNCaP and PC-3 cells using c-Myc–specific siRNA (100 nM) and analyzed for ClpP expression. (L) c-Myc was overexpressed in Hsp60-silenced LNCaP cells and analyzed for ClpP expression. Data are mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 by 2-tailed Student’s t test (C) or 1-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test (I). Actin serves as a loading control.