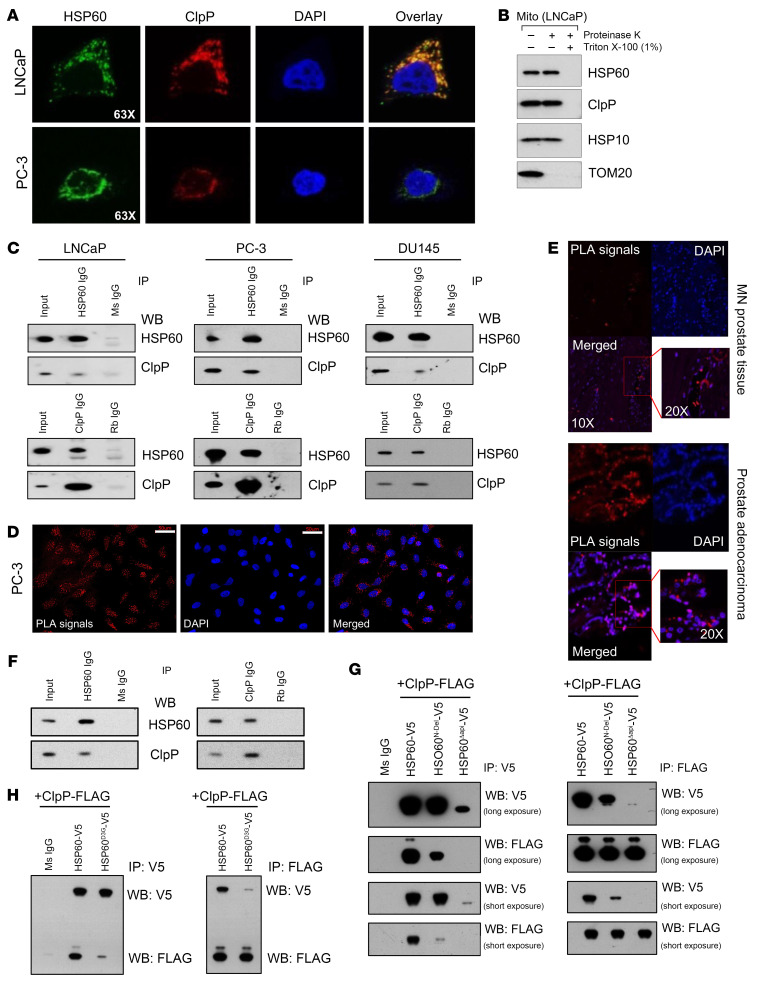
Figure 3. HSP60 and ClpP directly interact in mitochondria.
(A) Representative immunofluorescence images showing colocalization of HSP60 and ClpP. (B) Proteinase K and Triton X-100 digests were performed to determine HSP60, ClpP, and HSP10 colocalization in mitochondria (Mito). (C) Co-IPs were performed to determine HSP60 and ClpP interactions in LNCaP, PC-3, and DU145 cells. (D) Proximity ligation assay (PLA) between HSP60 and ClpP was performed in PC-3 cells. Scale bars: 50 μm. (E) PLA between HSP60 and ClpP was performed in TMA (n = 128) constructed from matched normal prostate (MN) and prostate adenocarcinoma tissue. (F) Co-IPs were performed to determine HSP60 and ClpP interactions in TKO prostatic tumor tissues. (G) Mitochondrial localization signal (HSP60N-Del) and apical domain (HSP60Δapi) were deleted from the HSP60 construct with a V5 tag and cotransfected with a ClpP construct with a FLAG tag in PC-3 cells. Co-IPs were performed using either anti-V5 antibody or anti-FLAG antibody. Ms IgG, control mouse IgG. (H) D3G mutant form of HSP60 (HSP60D3G) construct with V5 tag was cotransfected with the ClpP construct with a FLAG tag in PC-3 cells. Co-IPs were performed using either anti-V5 or -FLAG antibody. IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, Western blotting.