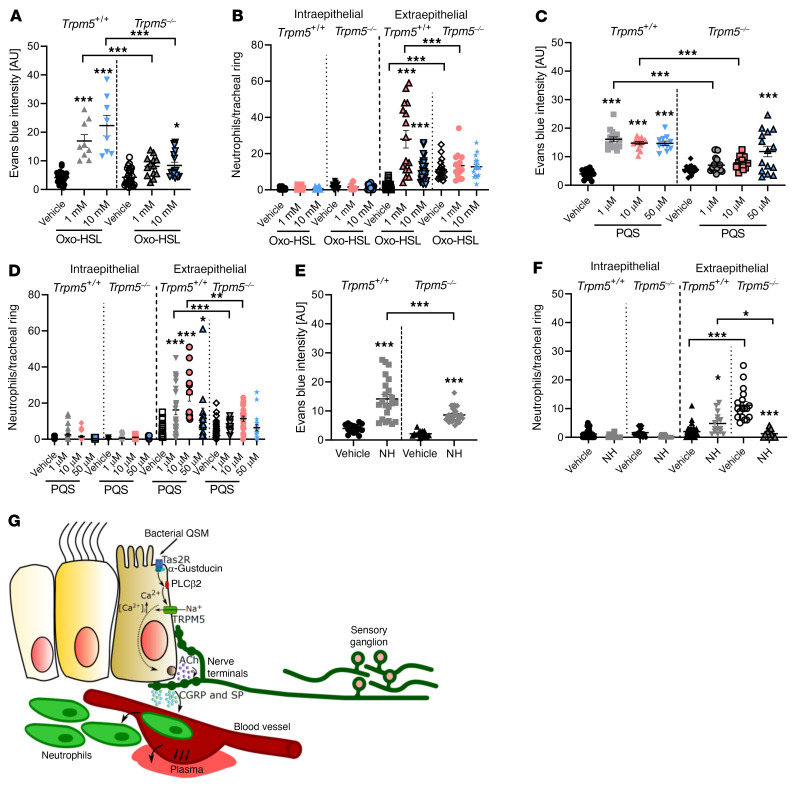
Figure 7. Evans blue (EB) extravasation and neutrophil recruitment in response to bacterial QSMs or bacterial culture supernatants.
(A, C, and E) Quantification of EB intensity in response to the QSMs N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone (Oxo-HSL) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal (PQS) as well as supernatants of the P. aeruginosa strain NH57388A (NH) in WT (Trpm5+/+) and Trpm5-deficient (Trpm5–/–) mice. (B, D and F) Analysis of intra- and extraepithelial neutrophils per tracheal ring in WT (Trpm5+/+) and Trpm5–/– mice. In A–F, data are shown as single values ± SEM (n = 8–30 rings from 3–5 mice). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 by 1-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple-comparison correction. (G) Proposed mechanism of induction of neurogenic inflammation after stimulation of the bitter signaling cascade in tracheal epithelial BCs with bitter or bacterial substances. Substances bind to bitter taste receptors, which activates α-gustducin, leading to Ca2+ release from intracellular stores that activates Trpm5 and ACh release from BCs. The released ACh then binds to ACh receptors on sensory neurons, leading to plasma extravasation and neutrophil recruitment via CGRP and SP release and to neurogenic inflammation.