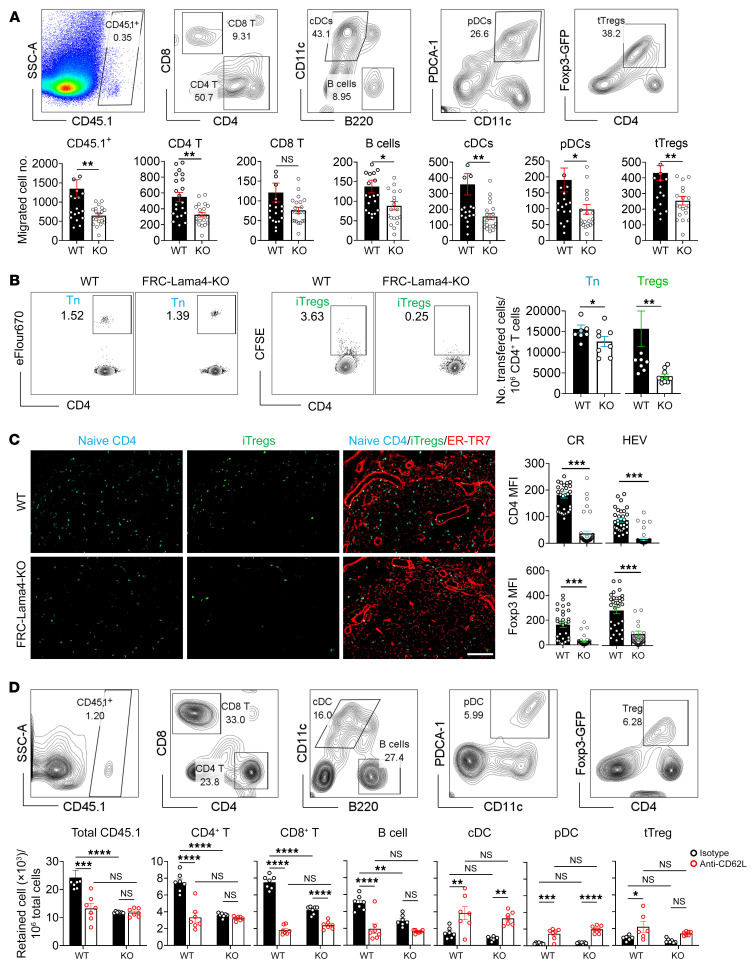
Figure 6. FRC-Lama4 depletion affects lymphocyte entry into LNs.
(A) 107 CD45.1+ splenocytes transferred i.v. into CD45.2+ WT and FRC-Lama4–KO recipients. After 1 hour, LNs were harvested and total migrated CD45.1+ cells, and CD45.1+ CD4+ T, CD8+ T cells, B cells, cDCs, pDCs, and Foxp3-GFP+ tTregs were counted in each LN. Gating strategy (upper) and data summary (lower) of migrated cells. (B and C) 2 × 106 CFSE+ iTregs and 2 × 106 eFlour 670+ CD4+ T cells transferred i.v. to FRC-Lama4–KO and WT mice. After 16 hours, LNs were harvested and transferred cells measured. (B) Flow cytometry gating strategy (left, values show percentage); number of transferred naive CD4+ T cells and iTregs relative to 106 total CD4+ T cells in LNs. (C) LN cryosections for CD4+ and iTregs and ER-TR7. Original magnification, ×20. Scale bar: 100 μm. Quantification of naive CD4+ T cells and iTregs in CR and HEV. (D) 107 CD45.1+ splenocytes transferred i.v. into CD45.2+ WT and FRC-Lama4–KO recipients. Eighteen hours later, recipients received 100 μg anti-CD62L mAb or isotype i.v. After an additional 18 hours, transferred cells in LNs were analyzed. Gating strategy (upper) and data summary (lower) of migrated cell frequency in recipient LNs. (A–D) Values in gating strategy show percentages. Representative of 3 independent experiments with 3 mice/group, 5 LNs/mouse, 3 sections/LN, and 3 to 5 fields/section. Student’s unpaired 2-tailed t test for 2-group comparisons. Two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons test. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. P < 0.05 was considered significant.