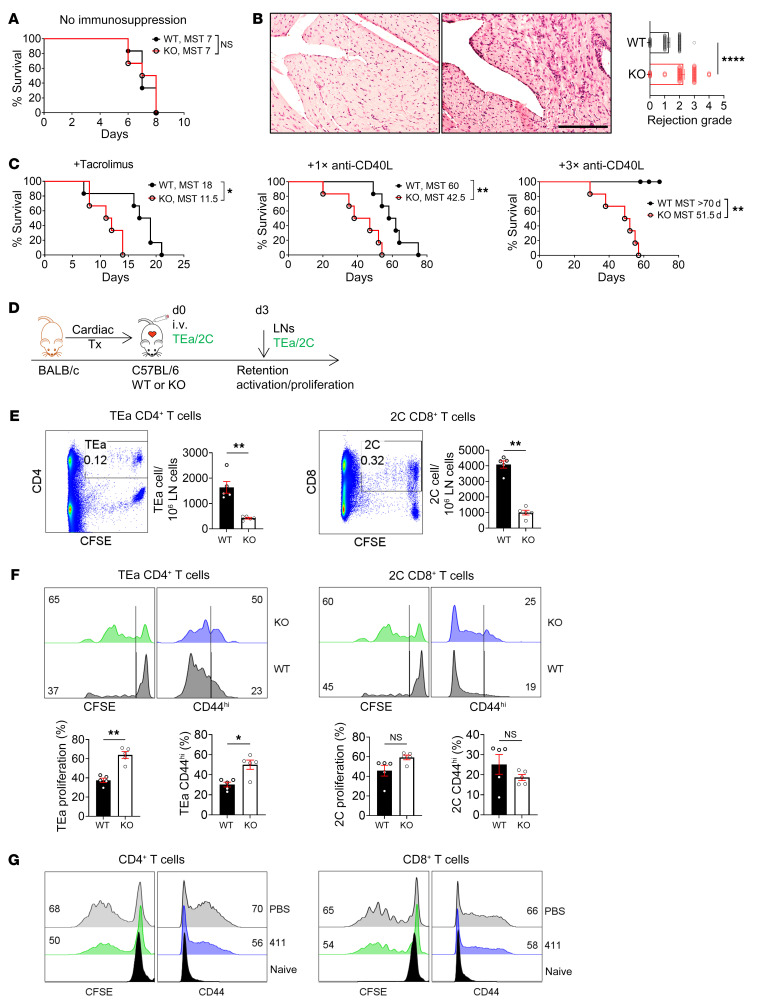
Figure 7. Ablation of FRC-Lama4 promotes T cell alloimmunity.
(A–C) C57BL/6 WT and FRC-Lama4–KO received BALB/c cardiac allografts. Allograft survival (A) without immune suppression or (C) with tacrolimus (2 mg/kg/day s.c.), 1 dose (1×, 250 μg, i.v. day 0), or 3 doses (3×, 250 μg/dose, i.v. days 0, 4, 7) of anti-CD40L mAb; log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test for graft survival, median survival time (MST), 6 mice/group. (B) H&E staining of heart grafts in WT (left) and FRC-Lama4-KO recipient mice (right) 3 days after transplantation, and rejection grade. Scale bar: 100 μm. (D–F) (D) Schematic of cardiac transplantation with adoptive transfer of alloantigen-specific TEa CD4+ and 2C CD8+ cells. CFSE-stained TEa plus 2C cells (each 2 × 106) injected i. v. into WT and FRC-Lama4–KO recipients on day 0. Recipient LNs harvested on day 3 to assess TEa and 2C cell numbers and responses. (E) Number, (F) proliferation, and CD44 expression at day 3. (G) CFSE+, CD4+, and CD8+ T cells cocultured with coated laminin 411 (2 μg/mL) or PBS and activated by coated CD3 mAb (5 μg/mL) and soluble CD28 mAb (1 μg/mL). CFSE and CD44 analyzed 3 days after activation. (E–G) Values show percentage. Data representative of 3 independent experiments; 3 mice/group. (B, E, and F) Student’s unpaired 2-tailed t test for 2-group comparisons. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001. P < 0.05 was considered significant.