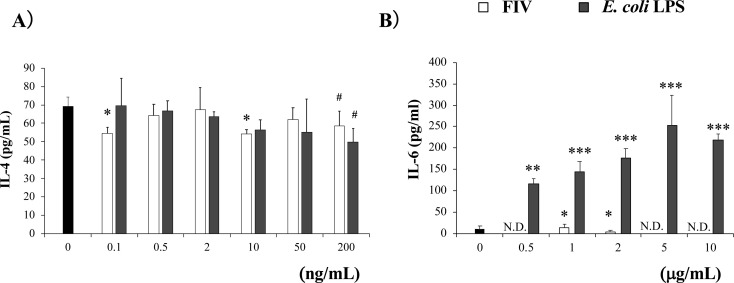
Fig. 3.
Purified LPS from G. hansenii GK-1 (FIV) inhibited the IL-4 production of spleen cells from food-allergic model mice, but did not induce IL-6 production of BALB/c spleen cells.
(A) OVA23-3 spleen cells were stimulated with LPS fraction extracted from FIV or E. coli LPS (final concentrations, 0.1, 0.5, 2, 10, 50, and 200 ng/mL) and OVA (final concentration 1 mg/mL). The cells were cultured for 24 hr, and the production of IL-4 in the collected supernatant was measured by ELISA. (B) BALB/c mouse spleen cells were stimulated with FIV and E. coli LPS (final concentrations, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, and 10 µg/mL). The cells were cultured for 24 hr, and the production of IL-6 in the collected supernatant was measured by ELISA. The cells were pooled for 3 mice, cultured and measured in 3 wells per each condition. Significance was determined by Dunnett’s test for each sample concentration vs a sample concentration of 0 ng/mL or 0 µg/mL (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, #p<0.1). LPS: lipopolysaccharide; OVA: ovalbumin; N.D.: not detected. The data are representative of two independent experiments.