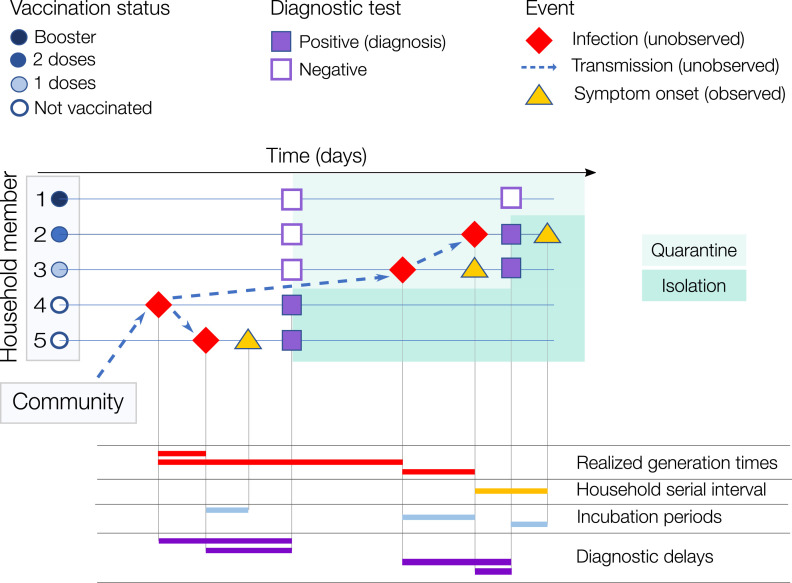
Figure 1.
Illustrative example of a household cluster. A household with 5 members, of which #4 (asymptomatic) was infected outside the household (in the general community) and then transmitted to cases #5 and #3 (both symptomatic). Case #3 infected #2 while #1 remained uninfected. #3, #2 and #1 were vaccinated with 1 dose, 2 doses, and 2 doses + booster respectively. In the bottom part of the figure, we show examples of the temporal intervals of interest for this work. Note that for the household serial interval and the realized household generation time, the source of infection (whether from outside the household or from a household member, and, in the latter case, which household member) is also unobserved and needs to be probabilistically reconstructed. The intrinsic generation time is not displayed as it represents the distribution of generation times among infections occurring in the general population in a fully susceptible population.11