Figure 4. Circulating EV concentration is increased in burn with inhalation injury as compared to similar burns without inhalation injury.
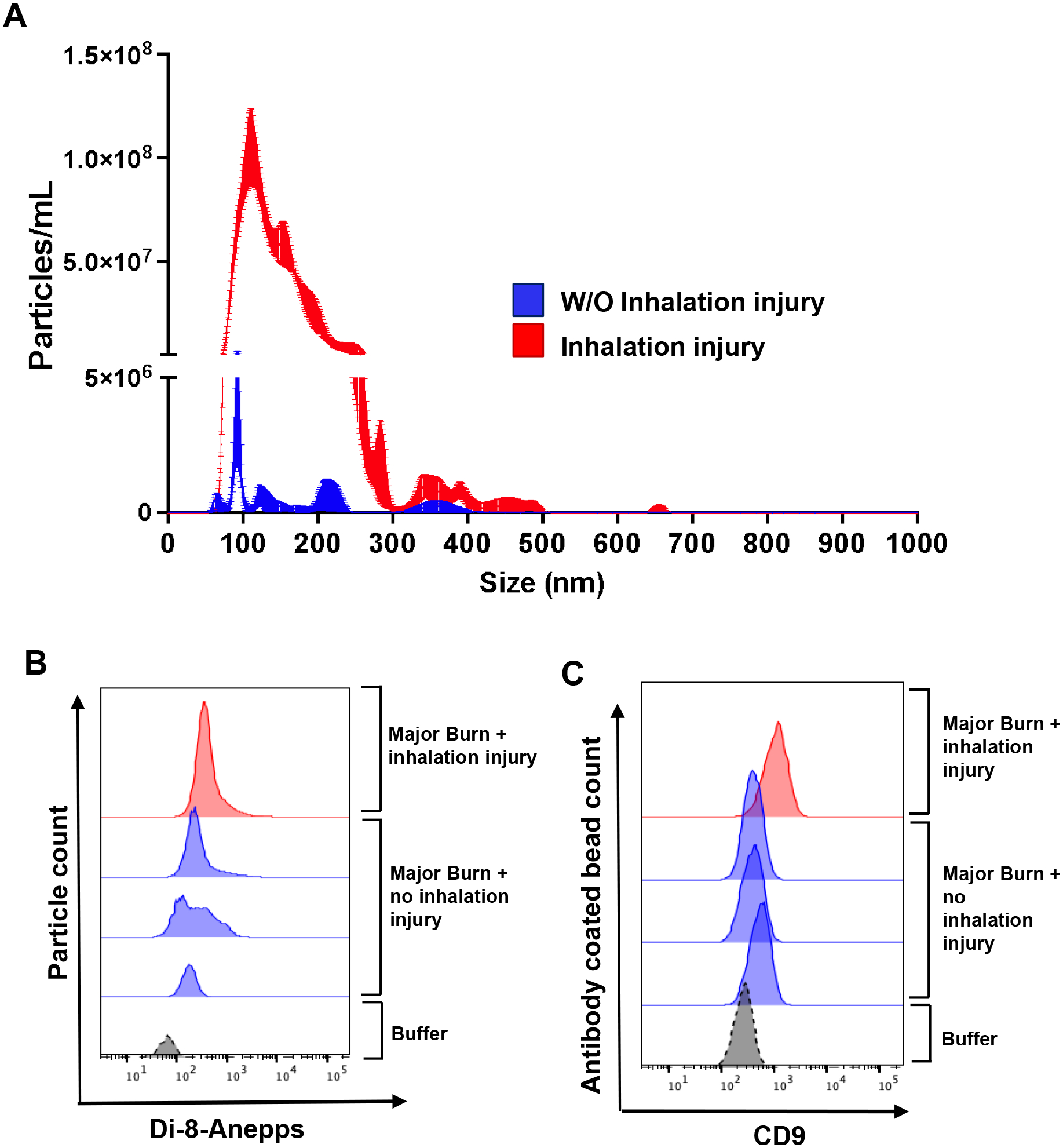
(A) Representative NTA tracing showing total EV numbers are increased in burn with inhalation injury (red) than in burn without inhalation injury (blue). (B-C) EVs measured by Di-8-Anepps+ staining (B) and CD9 immunocapture (B) are increased in burn patient with severe inhalation injury compared to patients with similar %TBSA burns but no inhalation injury. All burn patients examined have similar ~30%TBSA burns. N=3 burns without inhalation injury and n=1 burn with inhalation injury.
