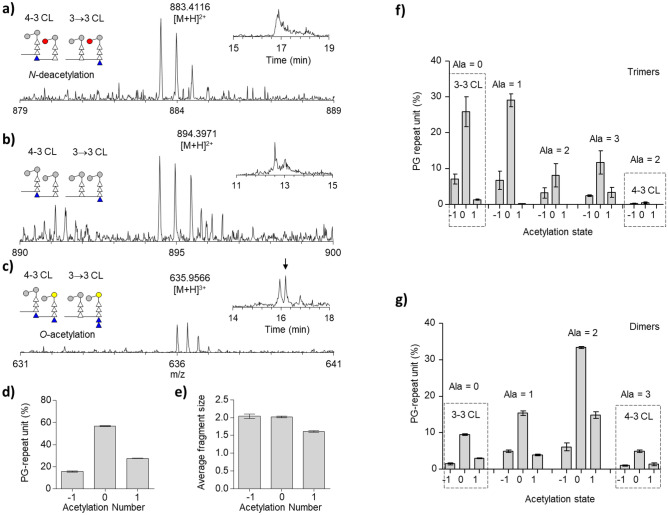
Figure 5.
Peptidoglycan acetylation of mc2155 cell walls. The PG disaccharide repeat unit, GlcNAc-MurNAc can be chemically modified by O-acetylation of MurNAc (+ 1) or N-deacetylation of GlcNAc (-1). (a–c) Mass spectra, XIC, and schematic representation of charged PG dimeric unit with acetylation states ranging from − 1 to + 1. Insets show a schematic representation of N-deacetylated and O-acetylated glycan as red and yellow-colored circles, respectively. The blue triangles represent D-Ala. Since the positions for O-acetylation and N-deacetylation have not been determined, the modification could have occurred in either GlcNAc or MurNAc. The cartoon representation excludes any other PG variation than net acetylation. The chemical structures of the representative MS are shown in Fig. S4. (d) Breakdown of each PG ion observed according to the number of acetylation states. The unmodified muropeptides fragments are found at 56.72 ± 0.49%, followed by O-acetylated muropeptides at 27.60 ± 0.25%, and N-deacetylated at 15.67 ± 0.47%. The composition is shown in Table S8. (e) Calculated average fragment size in muropeptide as a function of acetylation. (f) Degree of crosslinks in PG trimers calculated based on net acetylation. The composition is shown in Table S9. (g) Degree of crosslinks in PG dimers calculated based on net acetylation. The composition is provided in Table S12. All error bar represents a 95% confidence interval (n = 3) for technical error.