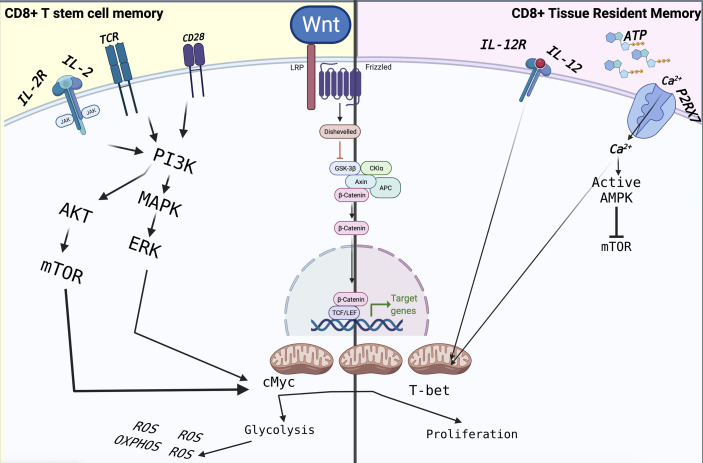
Figure 2.
The immunometabolism of TSCM and TRM is driven by extracellular factors, which are mainly based on mitochondrial respiration through FAO for their homeostasis. In particular, the metabolism of TRMs is based on the detection of extracellular ATP mediated by P2XR7, which controls their function and their survival. Following stimulation through TCR and CD28 in the presence of IL-2 and IL-12, CD8+ T cells activate reprogramming, differentiating into effector cells that will lead to the elimination of the pathogen or tumour cell. The signalling pathways are those of MAPK and mTOR, which lead to cell proliferation assisted by intense metabolic activity such as glycolysis and OXPHOS. The latter leads to the increased production of ROS, which will induce terminal differentiation and ultimately apoptosis, limiting the overall antitumor effect of CD8+ T cells.