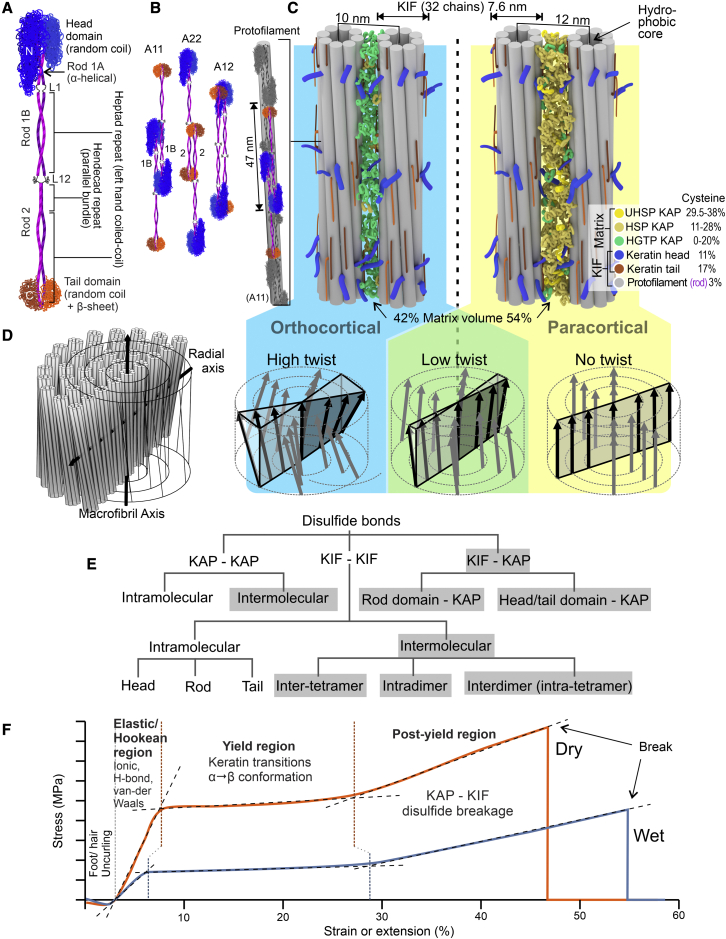
Figure 1.
Protein structure and mechanical properties of hair cortex. (A) Trichokeratin type I, type II dimer. (B) Variants of dimer relationships in tetramers and one example of a protofilament from end-to-end tetramers, with A11 representing the interaction of rod 1 regions of the heterodimers, A22 the interaction of the rod 2 regions, and A12 the interaction between rods 1 and 2. (C) Intermediate filament arrangement, relationship with matrix, and differences between orthocortex and paracortex. (D) Example of double-twist macrofibril and variation in twist intensity across cortex. (E) Disulfide bonds between and within key fiber components with inter-structural disulfide bonds highlighted. (F) The tensile behavior of wet versus dry stretched fibers. KIF, keratin intermediate filament; L1 linker 1; N, amino-terminus; C, carboxy-terminus; L12, linker 1,2; HGTP, high glycine-tyrosine protein; HSP, high sulfur protein; UHSP, ultra-high sulfur protein; KAP, keratin-associated protein. To see this figure in color, go online.