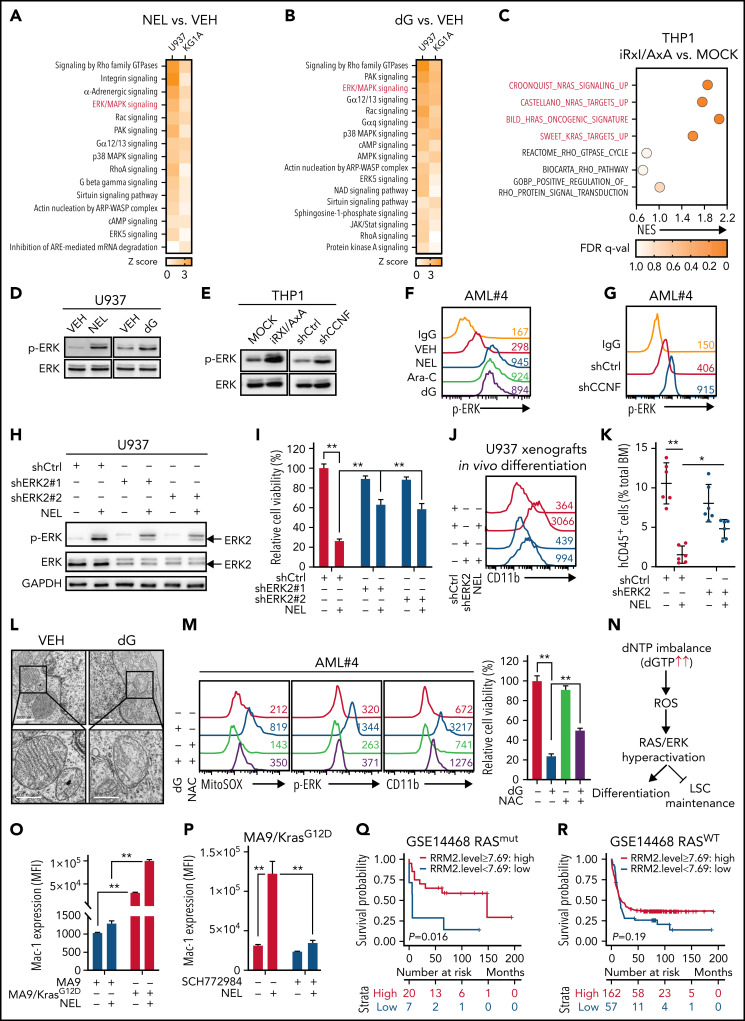
Figure 5.
ERK activation contributes to myeloid differentiation. (A-B) U937 or KG1A cells treated with or without NEL (10 µM, 24 hours) (A), with or without dG (10 µM, 24 hours) (B), were collected for RNA-seq analysis. Upregulated intracellular signaling pathways based on ingenuity pathway analysis (Z score > 0) were shown in both cell lines. ERK/MAPK pathway is highlighted in red. (C) Scattergrams of RAS GTPase-related gene sets (red) and Rho GTPase-related gene sets (black) based on enrichment analyses of differentially expressed genes in MOCK- and iRxl/AxA-THP1 cells after doxycycline induction. The color indicates the false discovery rate q values. NES, normalized enrichment score. (D) Western blot of phospho-ERK and total ERK levels in U937 cells treated with vehicle, NEL (10 µM) or dG (10 µM) for 24 hours. (E) Western blot of phospho-ERK and total ERK levels in MOCK- and iRxl/AxA-THP1 cells after doxycycline induction (i) and THP1 cells transduced with shCtrl or shCCNF lentivirus (ii). (F) Phospho-ERK levels in primary AML CD34+ cells from specimen AML#4 treated with vehicle, NEL (20 µM), Ara-C (0.5 µM), or dG (15 µM) for 24 hours. (G) Phospho-ERK levels in primary AML CD34+ cells from specimen AML#4 transduced with shCtrl or shCCNF lentivirus. (H) Western blot of the indicated proteins in U937 cells transduced with lentiviral vectors expressing shRNA against ERK2 (shERK2#1, shERK2#2 [chosen to be used further, namely shERK2]) or scramble control (shCtrl), followed by treatment with NEL (10 µM) for 24 hours. (I) Relative cell viability of U937 cells transduced with shCtrl, shERK2#1, or shERK2#2 lentivirus followed by treatment with NEL (10 µM) for 96 hours. Results represent mean ± SEM. **P < .01. (J-K) Representative CD11b expression (J) and percentages (K) of human CD45+ cells in BM of recipients (n = 6 per group) transplanted with shCtrl- or shERK2-U937 cells, followed by in vivo administration with vehicle (PBS) or NEL (217 mg/kg, IV, daily) for 7 days. For panel J, data from 1 representative mouse in each group are shown. For panel K, results represent mean ± SEM. *P < .05; **P < .01. (L) Transmission electron microscopy images of mitochondrial cristae in U937 cells treated with vehicle or dG (10 µM) for 24 hours. Scale bar, 1 µm (i) or 0.5 µm (ii). (M) Mitochondrial superoxide levels, phospho-ERK levels, CD11b expression levels, and relative cell viability of primary AML CD34+ cells from specimen AML#4 treated with vehicle, dG (15 µM), NAC (2 mM), or combination. Mitochondrial superoxide and phospho-ERK analyses were performed after treatment for 24 hours. CD11b expression and cell viability analyses were performed after treatment for 96 hours. For cell viability, results represent mean ± SEM. **P < .01. (N) A schematic diagram demonstrating the casual relationships among dNTP imbalance, mitochondrial ROS release, RAS/ERK hyperactivation, and differentiation/LSC maintenance. (O) Mac-1 expression levels in murine MA9+ and MA9/KrasG12D cells treated with vehicle or NEL (20 µM) for 96 hours. Results represent mean ± SEM. **P < .01. (P) Mac-1 expression levels in murine MA9/KrasG12D cells pretreated with SCH772984 (2 µM) for 6 hours, followed by treatment with NEL (20 µM) for 96 hours. Results represent mean ± SEM. **P < .01. (Q) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of a cohort of patients with AML (GSE14468) carrying RAS mutations after dichotomization for RRM2 mRNA levels below (blue, n = 7) and above (red, n = 20) 7.69 log2-transformed intensity (P = .016). (R) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of a cohort of patients with AML (GSE14468) carrying WT-RAS after dichotomization for RRM2 mRNA levels below (blue, n = 57) and above (red, n = 162) 7.69 log2-transformed intensity (P = .19).