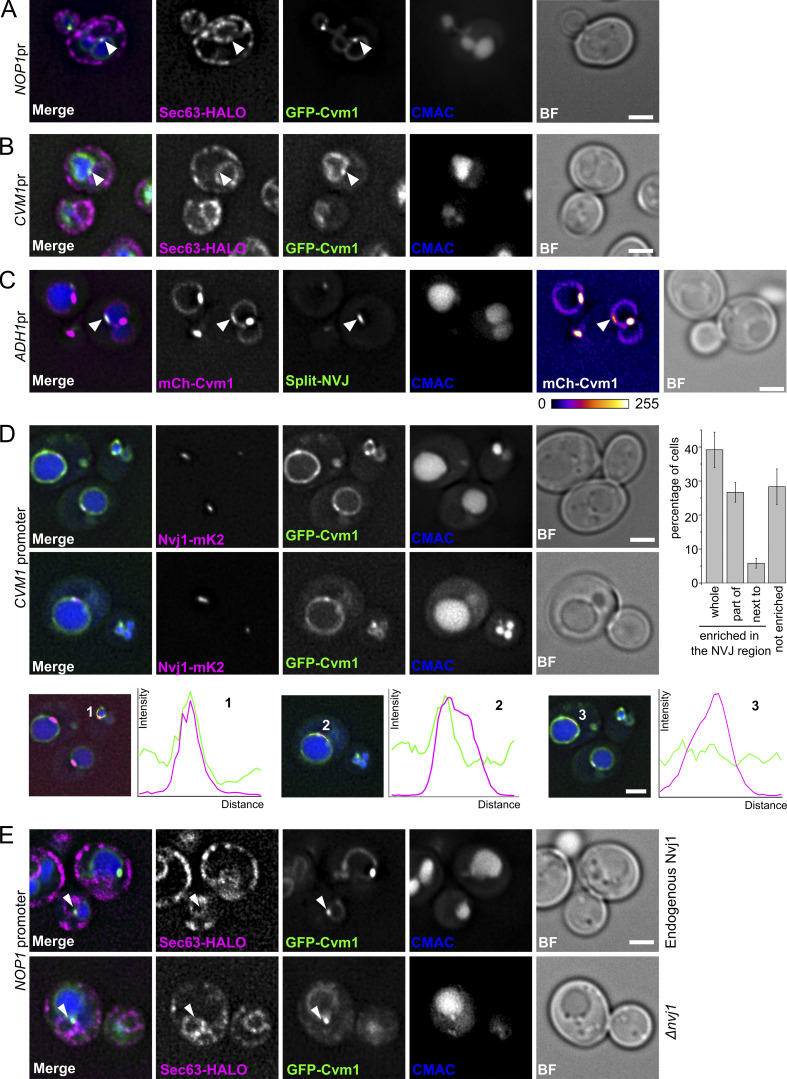
Figure 4.
Cvm1 localizes at the NVJ. (A and B) Fluorescence microscopy analysis of the localization of GFP-Cvm1 under the control of the NOP1 promoter (A) or the endogenous CVM1 promoter (B), Sec63-Halo stained with JF646 as a marker of the ER, and CMAC staining as a vacuolar marker. GFP-Cvm1 signal can be observed along the vacuole membrane, and accumulations of Cvm1 are observed in regions where the vacuole is closely apposed to the ER. Scale bar represents 2 µm. BF = Brightfield. (C) Fluorescence microscopy analysis of a split-NVJ reporter strain with mCherry-Cvm1 expressed under the control of the ADH1 promoter and CMAC as vacuolar staining. The split-NVJ reporter contains the VC fragment fused to the vacuolar protein Zrc1 and the VN fragment fused to the ER protein Sec63. Strong accumulations of Cvm1 do not colocalize with the reporter, but weaker accumulations of Cvm1 can be observed in regions positive for the reporter. mCherry-Cvm1 signal is shown with a Fire look-up table to make the enrichments of Cvm1 easier to observe. A bar showing the correspondence between intensity levels and color is shown below. Scale bar represents 2 µm. (D) Colocalization of Cvm1 with the NVJ marker Nvj1. Fluorescence microscopy images of a strain expressing GFP-Cvm1 under the control of the endogenous CVM1 promoter and Nvj1-mKate2 as a marker of the NVJ contact site. (1–3) Cvm1 localizes along the vacuole membrane. Some cells show enrichment of Cvm1 with the NVJ (1), whereas others show enrichment in a portion of the contact (2) or no enrichment (3), as shown by the line profiles along the vacuole membrane. The bar graph to the right shows the frequency of observation of the different phenotypes. Scale bars represent 2 µm. (E) Enrichment of Cvm1 in the vacuole–ER interface does not depend on Nvj1. Fluorescence microscopy analysis of the localization of GFP-Cvm1 under the control of the NOP1 promoter, Sec63-Halo stained with the JF646 ligand as a marker of the ER, and CMAC staining as a vacuolar marker. The experiment was performed in a strain containing the endogenous Nvj1 or a deletion of the gene. Accumulations of Cvm1 in regions of colocalization with the ER can still be observed in the absence of Nvj1.