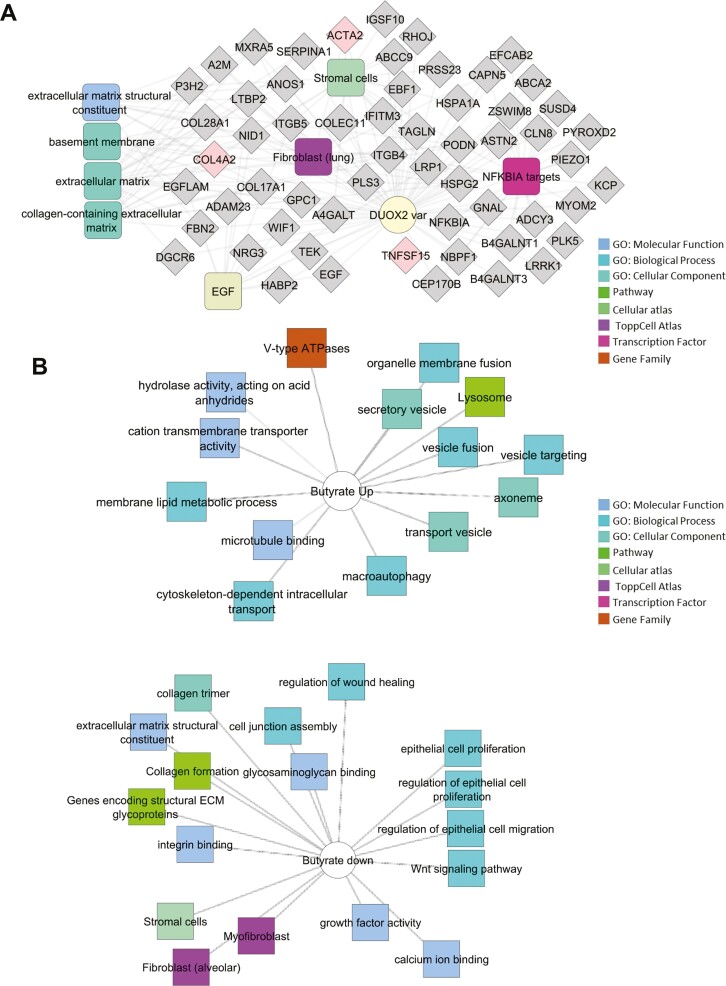
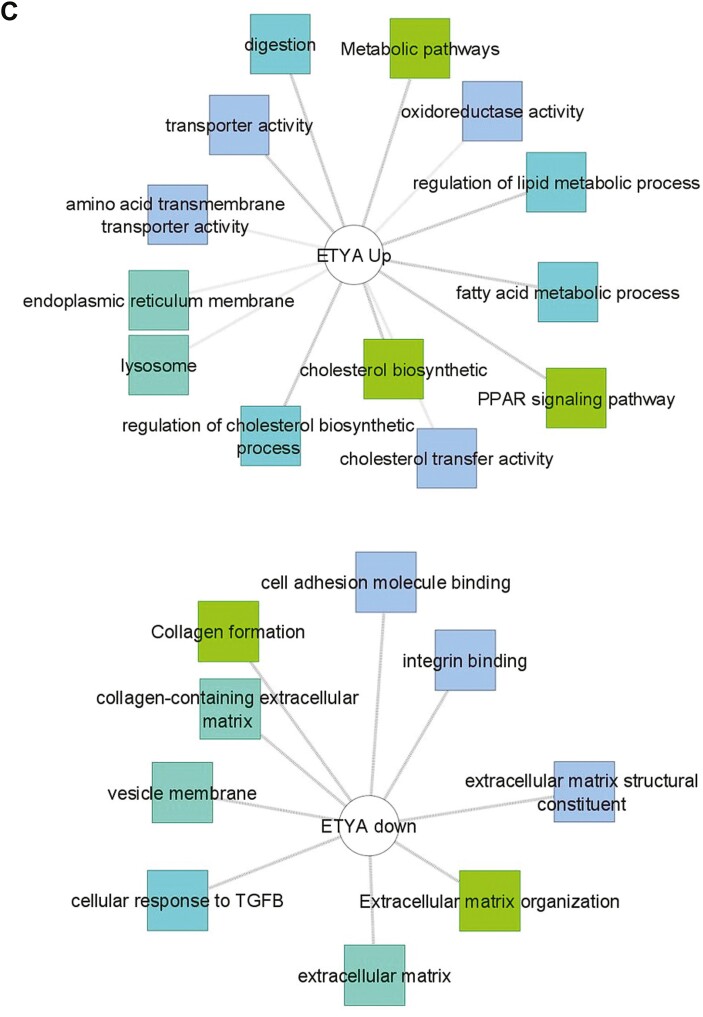
Figure 1.
Differentially expressed genes associated with DUOX2 genotype and butyrate or eicosatetraynoic acid (ETYA) exposure. A, Differentially expressed genes between DUOX2ref and DUOX2haplo human intestinal organoids (HIOs) were defined using bulk RNA sequencing (RNASeq) under basal conditions (n = 8 per group, with false discovery rate <0.05 and fold change ≥1.5). Functional annotation enrichment analysis of the 198 upregulated genes in the DUOX2hapl HIOs was completed using ToppGene, ToppCluster, and Cytoscape. Individual genes are shown in gray, with some highlighted in pink, with enriched signaling pathways, cell types, and biologic functions as shown. B, Differentially expressed genes between DUOX2ref HIOs under basal conditions and following 10 mM butyrate exposure for 72 hours were defined using bulk RNASeq (n = 4-8 per group, n = 8052 genes with false discovery rate <0.05 and fold change ≥1.5). Functional annotation enrichment analyses of the up- and downregulated genes were as shown. C, Differentially expressed genes between DUOX2ref HIOs under basal conditions and following 50 μM ETYA exposure for 12 days were defined using bulk RNASeq (n = 5-8 per group, n = 1383 genes with false discovery rate <0.05 and fold change ≥1.5). Functional annotation enrichment analyses of the up- and downregulated genes were as shown. ECM, extracellular matrix; GO, Gene Ontology; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; TGFB, transforming growth factor β.