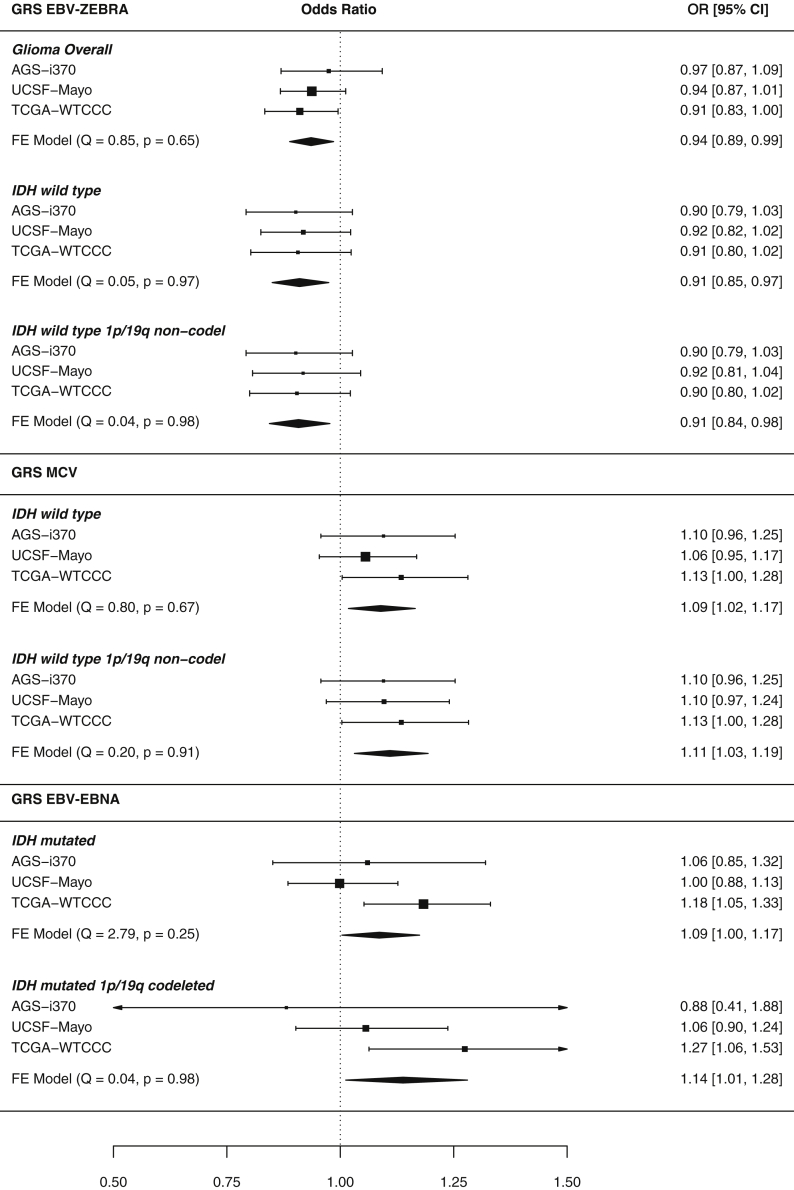
Figure 3.
Significant GRS-glioma subtype risk association meta-analysis forest plots
Forest plot meta-analysis results of GRS-glioma risk associations that were at least nominally statistically significant (p < 0.05). Response to antigens EBV ZEBRA, MCV, and EBV EBNA had associations that reached this threshold. Results are reported as odds ratios along with 95% confidence intervals. Briefly, each header indicates the studied viral antigen GRS, within are its association with molecular glioma subtypes reported with p < 0.05 and the 95% confidence interval of each study-specific effect. The diamond visualizes the 95% confidence interval for the fixed effect (FE) meta-analysis across all three studies. Each meta-analysis was tested for between-study heterogeneity (Q statistic), and p < 0.05 indicates evidence of study-specific associations.