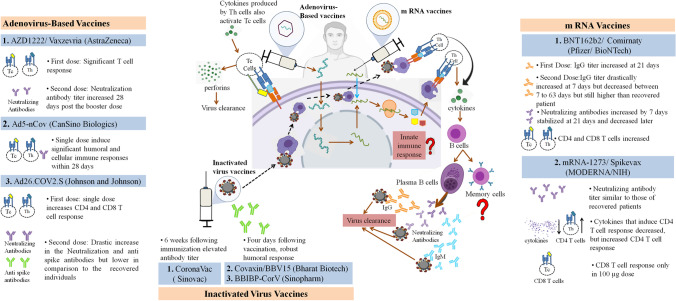
Fig. 2.
SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in development: Adenoviral vector vaccine (Vaxzevria, Ad5-nCov, and Ad26.COV2.S) - The adenovirus is designed to contain information encoding the wild type spike protein. As this modified adenovirus DNA enters the host cell, it uses the host machinery to translate the viral antigens which are presented to the T cells, leading to the activation of both Th and Tc cells. The Th cells produce cytokines that activate the B cells and Tc cells. The B cells differentiate into plasma B cells and memory B cells. The plasma B cells produce spike-specific IgG and IgM antibodies along with the neutralizing antibodies that play a major role in virus clearance. The Tc cells produce perforins that are also involved in virus clearance. mRNA-based vaccines (Comirnaty, and Spikevax)- The vaccine consists of an mRNA encapsulated in a lipid nanoparticle and has the information required to synthesize a stable prefusion of the spike protein. This m RNA when inside the host cells uses its machinery to translate the viral antigens, which are presented to the T cells, and thus activate the adaptive immune response against the Spike protein. Inactivated virus vaccine (CoronaVac, Covaxin, and BBIBP-CorV) - The inactivated whole virus when inside the host cell are presented by the APCs to the T cells which activate the adaptive immune response. The role of innate immune response and memory B cells in virus clearance still needs to be investigated.