Figure 3.
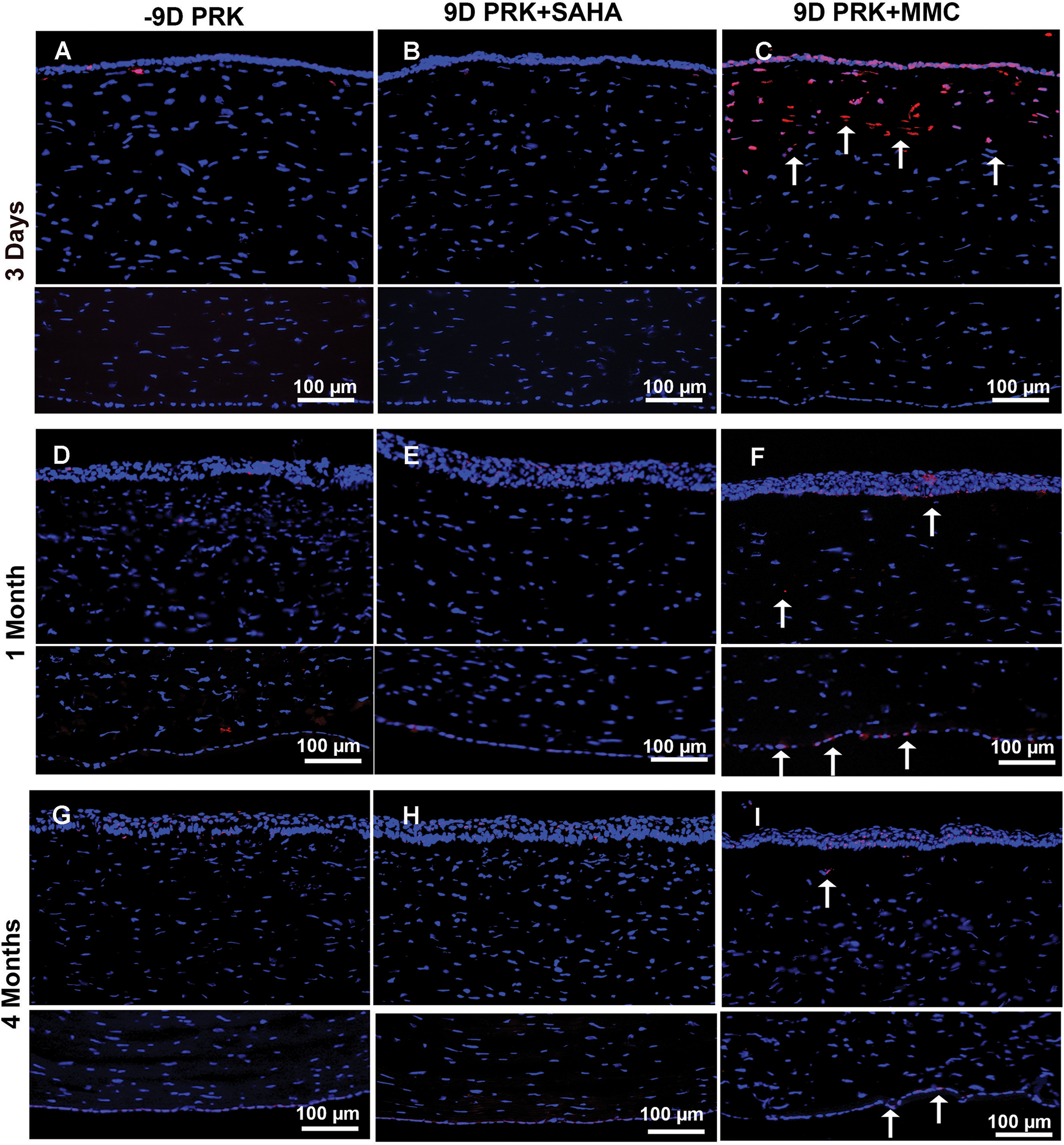
Effect of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) and mitomycin C (MMC) treatment on keratocyte and endothelial loss. Representative images showing TUNEL staining in rabbit corneas collected 3 days, 1 month, and 4 months after −9.00 diopter (D) photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) and balanced salt solution (BSS), SAHA (25 μM), or MMC (0.02%) single adjunct topical application. BSS (A, D, and G) or SAHA (B, E, and H) treatment did not induce apoptosis in corneal keratocyte or endothelial cells as shown by detection of no TUNEL+ cells. Conversely, MMC treatment (C, F, and I) provoked significant apoptosis in keratocyte and epithelial cells but none in endothelial cells at 3 days (C), with noticeable apoptosis in endothelial cells and some in keratocytes at 1 (F) and 4 (I) months as shown by arrows. These data suggest that MMC caused significant damage to anterior stroma and restricted keratocyte revival in this region lost in the first 3 days of MMC application. Nuclei are stained blue with DAPI. TUNEL+ cells are stained red (arrows). Scale bar = 100 μm
