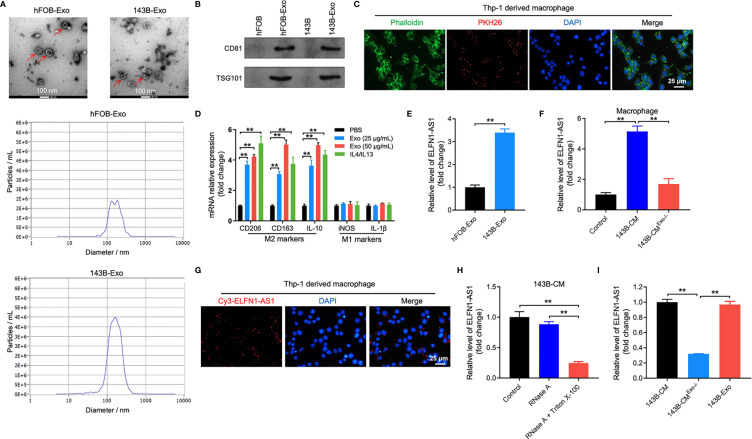
Figure 3.
ELFN1-AS1 could be delivered to macrophages by exosomes. (A) Exosomes were isolated from the hFOB and 143B cell CM. The size of exosomes was assessed by NTA assay. The morphology of exosomes was observed by TEM at 100 keV. Red arrow, exosomes. (B) The expression of exosome surface markers CD81 and TSG101 were determined by western blot assay (n = 3). (C) PKH26-labeled exosomes from 143B cells absorbed by macrophages were observed under fluorescence microscope (n = 3). (D) RT-qPCR analysis of CD206, CD163, IL-10, iNOS, IL-1β in macrophages treated with indicated exosomes or IL4/IL13 (n = 3). (E) ELFN1-AS1 level in exosomes isolated from CM of hFOB and 143B cells were detected using RT-qPCR (n = 3). (F) RT-qPCR analysis of ELFN1-AS1 level in macrophages incubated with CM, 143B cell-CM, exosome-depleted 143B cell-CM (n = 3). (G) Cy3-tagged ELFN1-AS1 labeled 143B cells were co-cultured with macrophages for 48 h. Meanwhile, the fluorescence signal in macrophages was observed by microscopy (n = 3). (H) RT-qPCR analysis of ELFN1-AS1 level in the CM of 143B cells (n = 3). (I) RT-qPCR analysis of ELFN1-AS1 level in 143B cell-Exo, 143B cell-CM, exosome-depleted 143B cell-CM (n = 3). The significance between two groups was analyzed by Student’s t test or one-way ANOVA respectively. **P < 0.01.