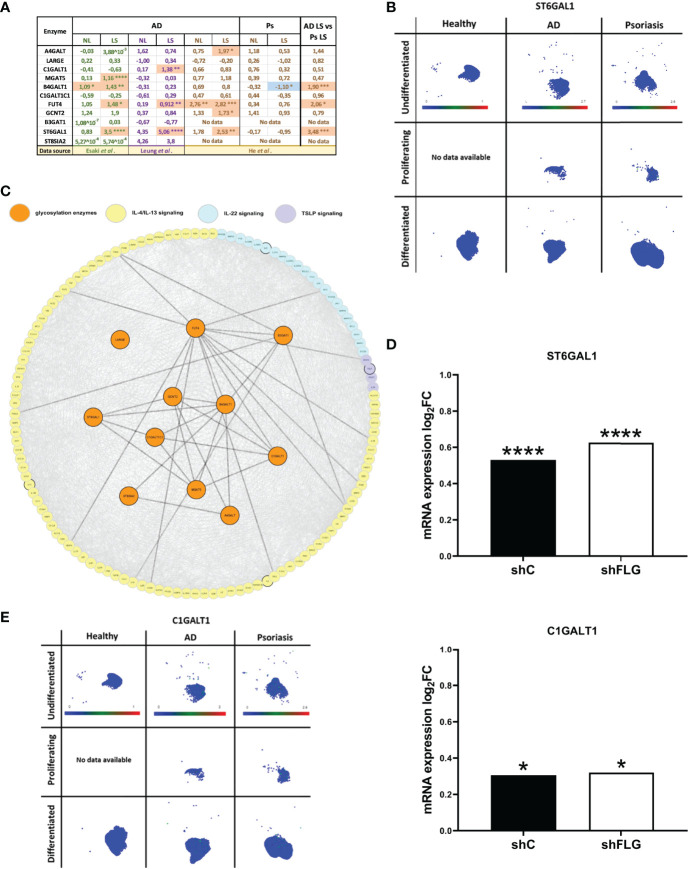
Figure 4.
Glycosylation enzymes are upregulated in the epidermis of AD patients and keratinocytes exposed to AD milieu. (A) The expression of glycosylation enzymes in the epidermis of AD and Ps patients; analysis of the transcriptome profiling data available as datasets in Esaki et al., Leung et al. and He et al. (values in the table show expression log2FC compared to healthy epidermis); *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; (moderated t-test for Esaki et al. and He et al., multiple unpaired t-tests for Leung et al.); NL, non-lesional epidermis; LS, lesional epidermis; (B) UMAP plots of single cell expression of ST6GAL1 enzyme in keratinocyte subpopulations in the skin; data available through Human Developmental Cell Atlas; (C) protein network links between AD-relevant cytokine pathways and the previously identified 11 glycosylation-relevant enzymes; (D) mRNA expression of glycosylation enzymes differentially regulated upon exposure to IL-4/IL-13 stimulation in filaggrin-insufficient (shFLG; knockdown) keratinocytes and control (shC) keratinocytes (log2 fold change shown); combined data for n=3 biological replicates; *p < 0.05; ****p < 0.0001 (moderated t-test); (E) UMAP plots of single cell expression of C1GALT1 enzyme in keratinocyte subpopulations in the skin; data available through Human Developmental Cell Atlas; ST6GAL1, β-Galactoside α-2,6-Sialyltransferase 1; C1GALT1, Core 1 β,3-Galactosyltransferase 1.