Fig. 1.
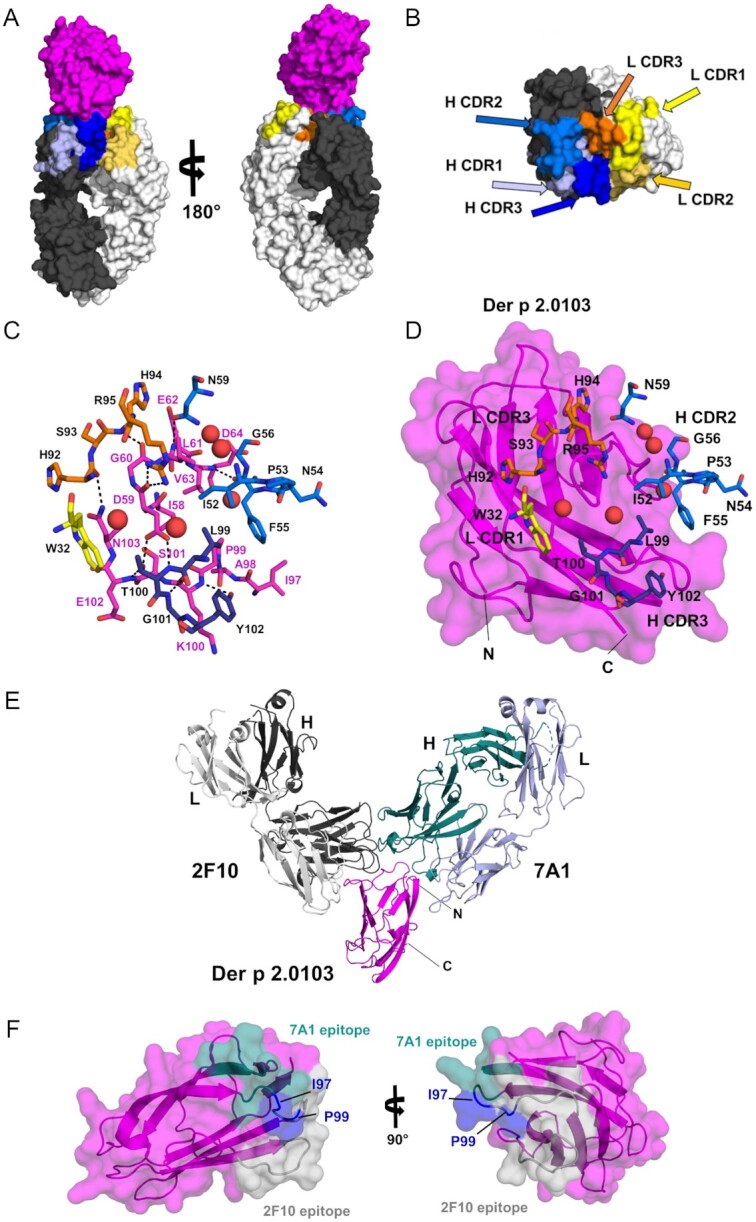
X-ray crystal structure of Der p 2 in complex with Fab of the IgE mAb 2F10. (A) Overall structure of Der p 2.0103 in complex with IgE mAb 2F10 Fab, shown in space filling representation. Der p 2 is shown in magenta, whereas light and heavy chains of the Ab are marked in light and dark gray, respectively. (B) The Complementarity Determining Regions (CDRs) of the heavy and light chains of the antibody are mapped on the molecular surface of IgE mAb 2F10 Fab, colored as in section A and labeled. (C) Residues forming the epitope and the paratope, responsible for allergen–antibody interactions are presented in stick representation and labeled in magenta and black, respectively. Water molecules buried between the allergen and the antibody are shown as red spheres. Colors are consistent with the images in (A) and (B). (D) Same area and molecular orientation as in (C), with the addition of Der p 2.0103 (magenta), shown in space filling and cartoon representations. Several 2F10 residues, including the ones responsible for interactions with the allergen, are presented in stick representation and labeled in black. (E) Superposition of the human 2F10 IgE mAb and the murine 7A1 IgG mAb Fabs binding to Der p 2.0103 to assess the relative location of their epitopes, shown in (F). (F) Surface of Der p 2.0103 with 7A1 and 2F10 epitopes marked in teal and gray, respectively. Ile97 and P99 (marked in blue) belong to both epitopes. The model of the allergen is derived from the Der p 2.0103–2F10 Fab complex structure.
