Figure 1. Characterization of JBJ-09-063 in enzymatic assays, in vitro BaF3 cellular studies and in vivo xenograft models.
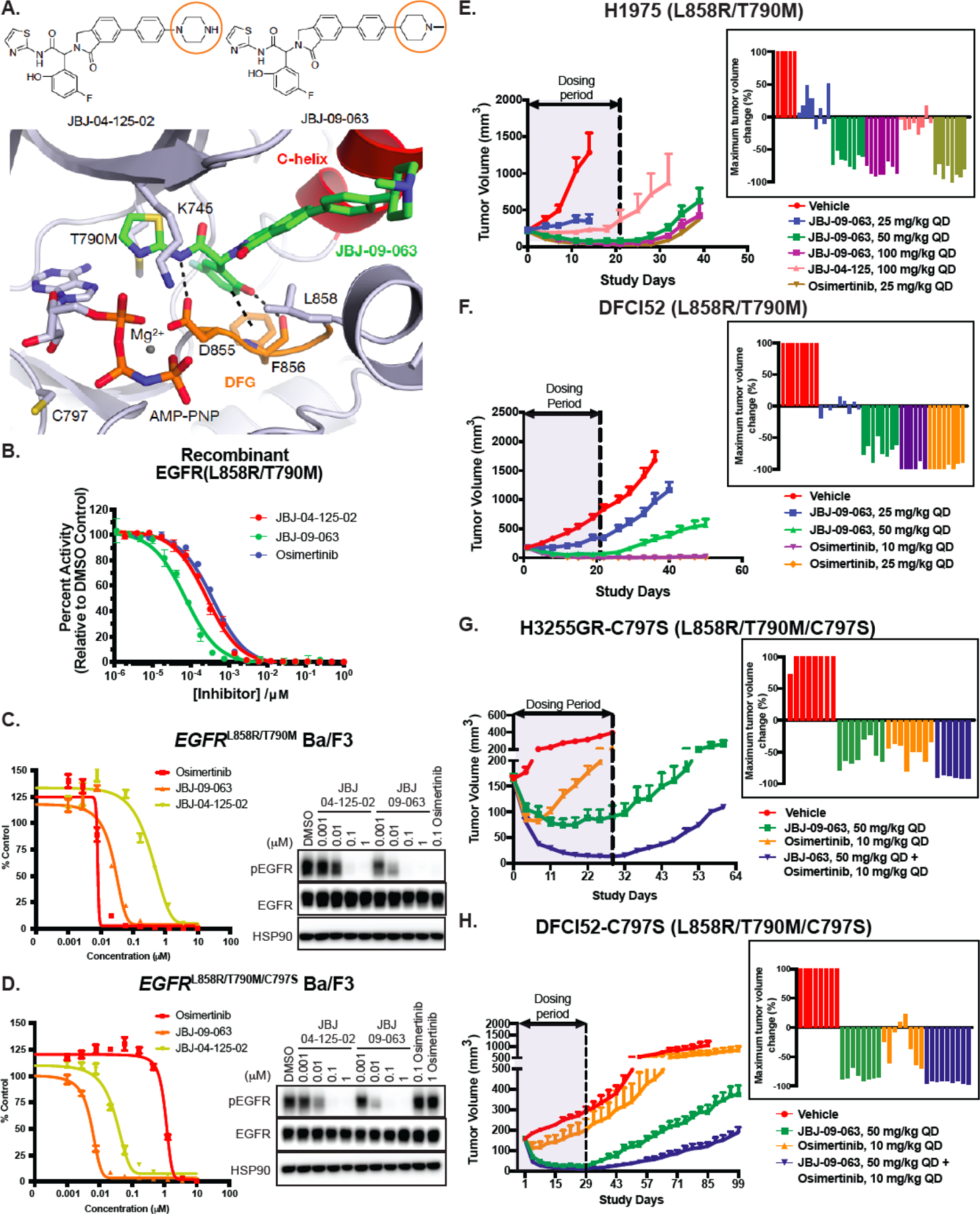
(A) Chemical structures of JBJ-04-125-02 and JBJ-09-063 with orange circles depicting the key difference between the two molecules. The 1.8 Å co-crystal structure of JBJ-09-063 in complex with EGFRT790M/V948R confirming an allosteric binding mode (PDB 7JXQ). JBJ-09-063 forms a critical hydrogen bond with D855 and a pi-stacking interaction with F856 in the DFG motif. (B) In vitro enzymatic inhibition assay of recombinant EGFR L858R/T790M kinase domain treated with increasing concentrations of allosteric inhibitors, JBJ-04-125-02, JBJ-09-063 and osimertinib. Results is graphed as percentage activity relative to DMSO control (mean ± SD). Cell growth and EGFR phosphorylation inhibition activity of JBJ-04-125-02 and JBJ-09-063 in (C) EGFRL858R/T790M and (D) EGFRL858R/T790M/C797S Ba/F3 cells as measured by Cell Titer Glo assay and Western Blot. Cell proliferation was graphed as a percentage relative to DMSO control. Data shown in A-C are representative experiments that were repeated at least three times. Efficacy studies examining the effect of allosteric inhibitors (JBJ-09-063, JBJ-04-125-02) and tyrosine kinase inhibitor (osimertinib) in (E) H1975 and (F) DFCI52 xenograft models harboring the EGFRL858R/T790M mutation. Efficacy studies examining the effect of JBJ-09-063 or osimertinib as a single agent or in combination in (G) H3255GR-C797S and (H) DFCI52-C797S xenograft models harboring the EGFRL858R/T790M/C797S mutation. Data is shown as a group mean of tumor volume in mm3 ± SEM relative to the start of treatment for all available data at the indicated timepoint (Study Days) with corresponding waterfall plots indicating maximum response in each group.
