Figure 2. JBJ-09-063 efficacy in human cancer cells is enhanced when combined with gefitinib.
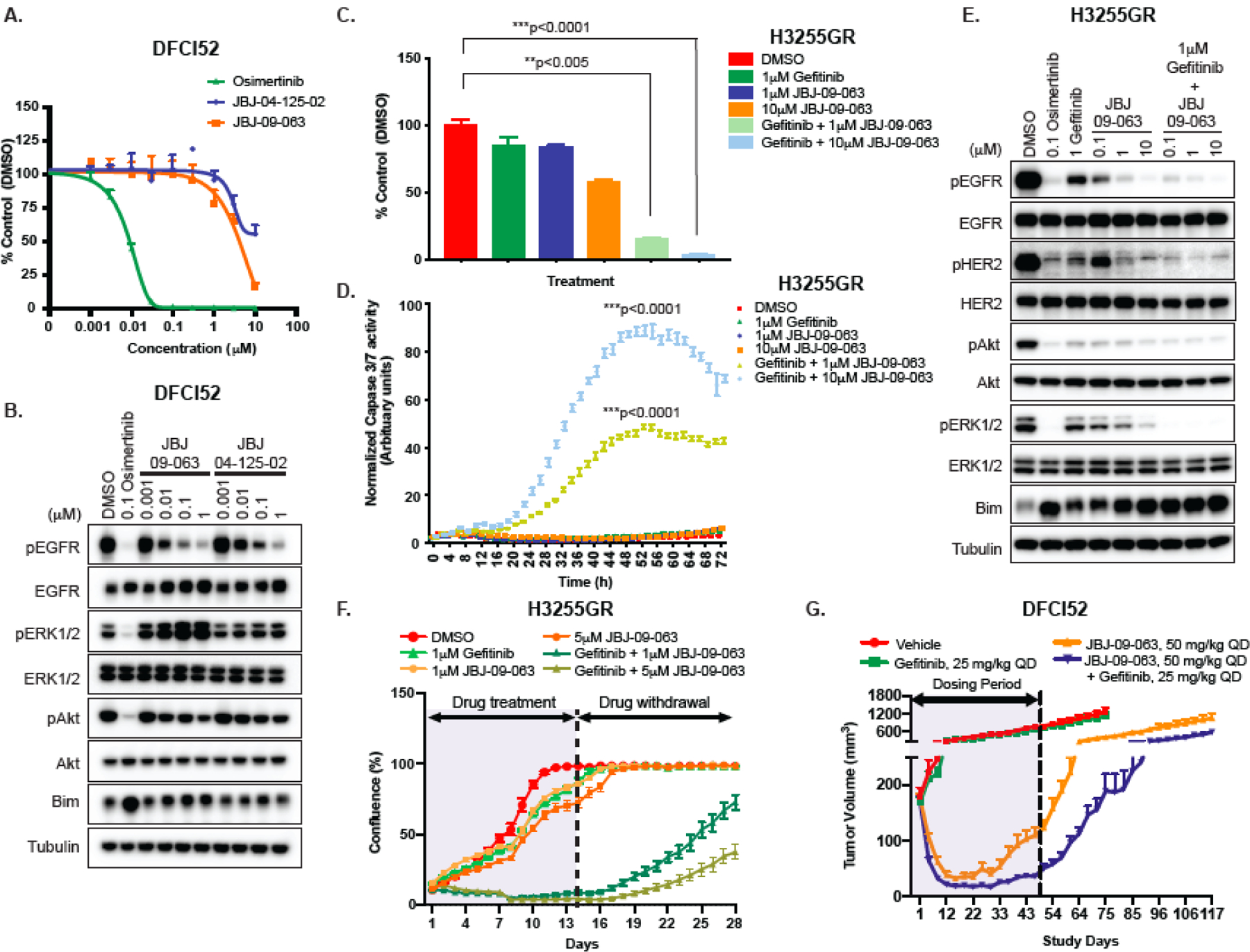
(A) Cell viability and (B) Western Blot analyses of DFCI52 cells treated with indicated concentrations of osimertinib, JBJ-09-063 and JBJ-04-125-02. (C) Cell viability and (D) apoptosis measured as normalized Caspase3/7 activity and (E) Western Blot analyses of H3255GR cells treated with indicated concentrations of gefitinib, JBJ-09-063 and the combination of both agents. (F) Long-term cell growth assay measured as confluency (%) in H3255GR cells treated with indicated concentrations of gefitinib, JBJ-09-063 and the combination of both drugs for two weeks followed by drug withdrawal for an additional two weeks. Data shown in A-F a representative experiment that was repeated at least two times. All cell viability assays were graphed as a percentage of activity relative to DMSO control over indicated concentrations and all apoptosis experiments were graphed as normalized caspase 3/7 activity (in arbitrary units) over time. Statistical significance was determined using a one-way ANOVA on ranks (the Kruskal-Wallis Test) and Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. **P<0.005; ***P<0.0001. (G) Efficacy studies examining the effect of JBJ-09-063 as a single agent or in combination with gefitinib in DFCI52 xenograft model harboring the EGFRL858R/T790M mutation. Data is shown as a group mean of tumor volume (mm3) ± SEM relative to the start of treatment for all available data at the indicated timepoint (Study Days).
