Figure 1.
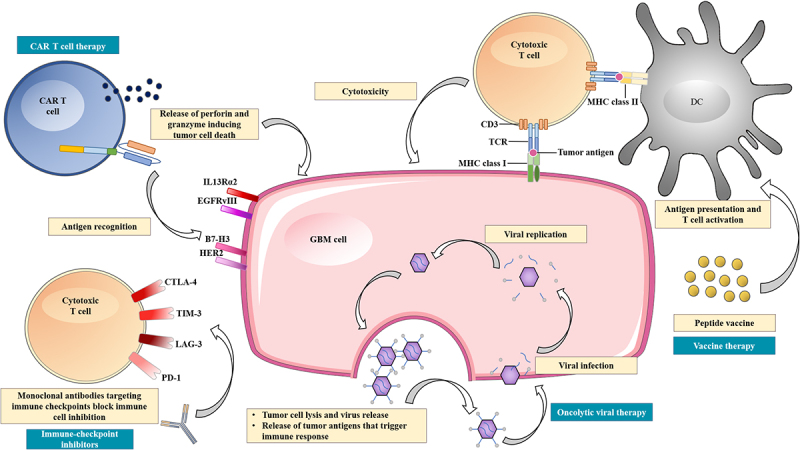
Overview of the current immunotherapeutic modalities for the treatment of glioblastoma.
CAR T cell therapy can target antigens that are highly expressed on GBM cell surfaces, including IL13Rα2, EGFRvIII, B7-H3, and HER2. Oncolytic viral therapy utilizes genetic engineered viruses that can selectively infect and replicate in GBM cells, leading to cell lysis and release of tumor antigens. This can further trigger an adaptive antitumor immune response by stimulating antigen presenting cells. Vaccine therapy depends on dendritic cells, which present antigens or peptides to cytotoxic T cells via MHC class II-TCR interaction resulting in T cell activation. Then, the cytotoxic T cells eradicate GBM cells via MHC class I-TCR interaction. This process, however, can be suppressed by upregulation of immune checkpoint ligands that can bind to various receptors on cytotoxic T cells. Immune checkpoint inhibitors are monoclonal antibodies that target immune checkpoints, such as PD-1, CTLA-4, TIM-3, and LAG-3, thereby blocking immune cell inhibition.
