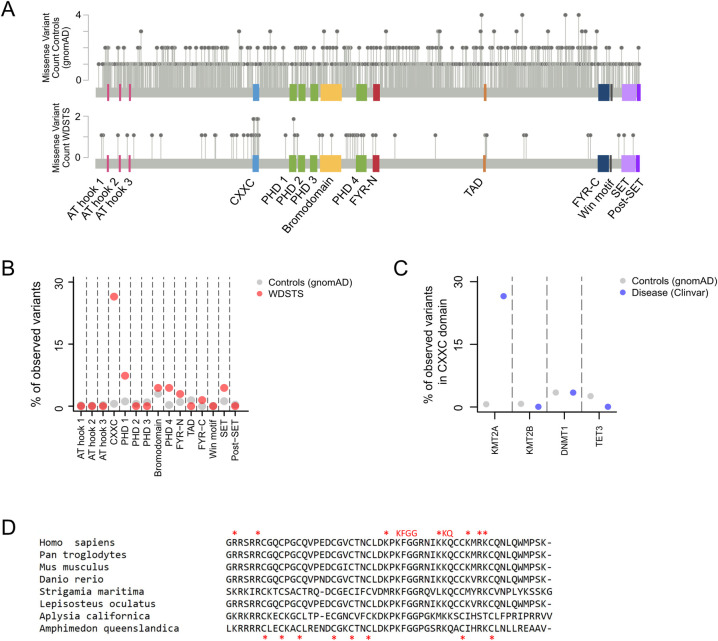
Fig 1. The distribution of likely pathogenic Wiedemann-Steiner syndrome missense variants across the different domains of KMT2A.
(A) KMT2A missense variants in gnomAD (top) and WDSTS (bottom). See Methods for filtering criteria. (B) The percentage of missense variants from gnomAD (grey dots) and WDSTS (red dots) that fall in each of the different domains of KMT2A. (C) The percentage of missense variants in gnomAD (grey dots) and likely pathogenic variants (blue dots) that fall in the CXXC domain of different epigenetic regulators. (D) Multiple sequence alignment of the amino-acid sequence of the CXXC domain of KMT2A in eight eukaryotic species. Residues known to be important for DNA binding are marked with red asterisks at the top (see Methods for details). The eight zinc ion-binding cysteines are marked with red asterisks at the bottom.